Introduction
India, a land of vibrant culture and diverse cuisine, faces a significant challenge: protein deficiency in India.
While the country has made strides in addressing hunger, the quality of nutrition remains a concern, particularly regarding protein intake.
Protein is a fundamental building block of life, and its deficiency can lead to a cascade of health problems, especially in vulnerable populations like children and vegetarians.
This blog aims to shed light on the pervasive issue of protein deficiency in India, its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Why is Protein So Important?

Think of protein as the construction crew of your body. It involves almost every bodily function, from building and repairing tissues to producing enzymes and hormones. Here’s a breakdown of its crucial roles:
- Building Blocks: Protein comprises amino acids, the building blocks of muscles, bones, skin, hair, and organs. Without enough protein, these structures can weaken and deteriorate.
- Enzyme and Hormone Production: Enzymes are catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in the body, and hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various functions. Both rely on protein.
- Immune System Support: Antibodies, which fight off infections, are made of protein. A protein deficiency weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses.
- Transportation and Storage: Protein helps transport oxygen, nutrients, and other substances throughout the body. It also plays a role in storing certain nutrients.
- Maintaining Fluid Balance: Protein helps maintain the proper balance of fluids in the body.
- Energy Source: While carbohydrates and fats are the primary sources of energy, protein can also be used for energy when needed.
In essence, protein is essential for growth, development, and overall health.
How Does Protein Deficiency Affect Children?

Children are particularly vulnerable to protein deficiency because they rapidly grow and develop. Insufficient protein intake can have severe consequences:
- Stunted Growth: Protein is crucial for building tissues and bones. A deficiency can lead to stunted growth and delayed development.
- Kwashiorkor: This severe form of protein malnutrition is characterized by edema (swelling), particularly in the abdomen, due to fluid retention. Other symptoms include skin lesions, hair discoloration, and irritability.
- Marasmus: This condition results from severe deficiency of both protein and calories. Children with marasmus are extremely thin and wasted, with little or no body fat. They are also prone to infections.
- Impaired Cognitive Development: Protein is essential for brain development. Deficiency can lead to cognitive deficits, learning difficulties, and behavioral problems.
- Weakened Immune System: Children with protein deficiency are more susceptible to infections like diarrhea, pneumonia, and measles.
- Increased Mortality: Severe protein malnutrition significantly increases the risk of death in children.
Addressing protein deficiency in children is crucial for their physical and cognitive development, ensuring a healthy future.
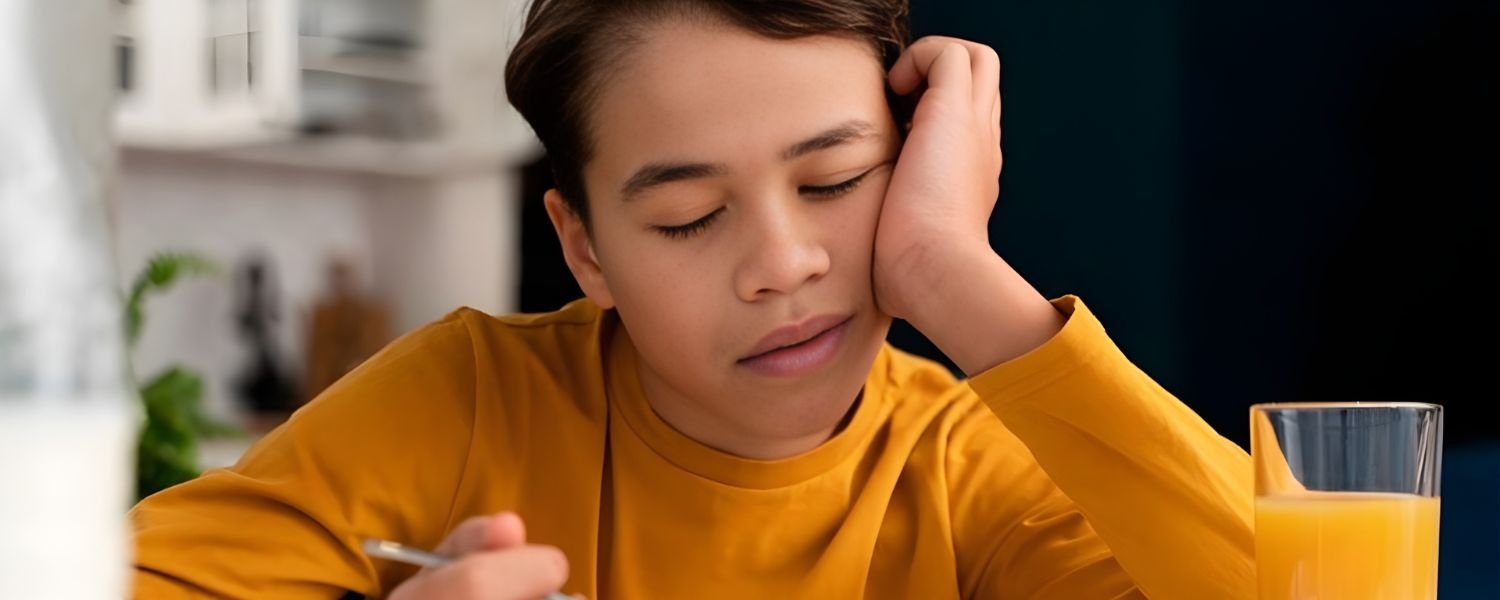
Which Protein Is for Children?

When selecting protein sources for children, it’s important to focus on high-quality proteins that provide all the essential amino acids. These include:
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are excellent sources of protein and calcium, crucial for bone development.
- Eggs: Eggs are a complete protein source, meaning they contain all the essential amino acids.
- Lean Meats: Chicken, fish, and lean red meat are good sources of protein and iron.
- Pulses and Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans are excellent plant-based protein sources, especially important for vegetarian children.
- Soy Products: Tofu and soy milk are good protein and other nutrient sources.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds provide protein and healthy fats.
It’s important to offer a variety of protein sources to ensure children get all the essential amino acids and other nutrients they need.
Which Foods Can Help Combat Protein Malnutrition Diseases?
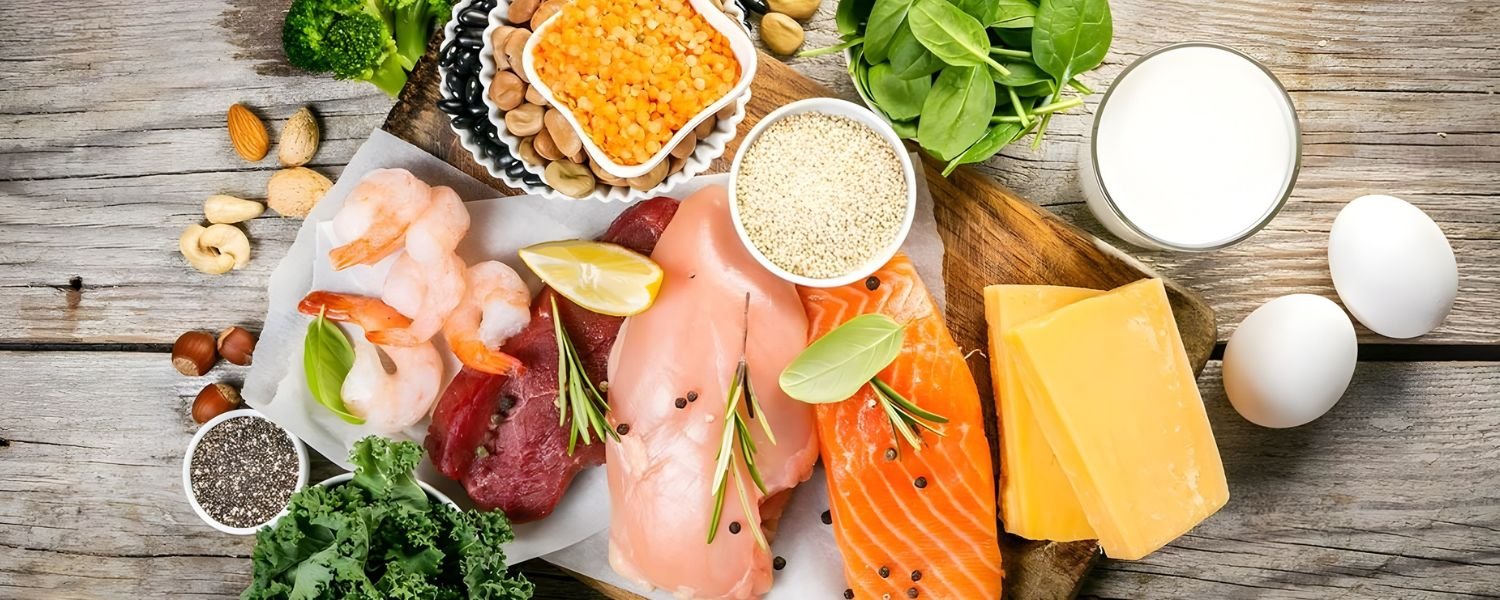

Combating protein malnutrition requires a multi-faceted approach, focusing on increasing protein intake through a balanced diet. Here are some key food groups and specific foods:
- Pulses and Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans, and black beans are excellent plant-based protein sources. They are also rich in fiber, iron, and other essential nutrients.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese provide high-quality protein and calcium. Fortified dairy products can also provide vitamin D, essential for calcium absorption.
- Eggs: Eggs are a complete protein source and are easily digestible. They are also rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Soy Products: Tofu, tempeh, and soy milk are good protein and other nutrient sources. They are particularly important for vegetarian and vegan diets.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide protein, healthy fats, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats contain some protein and are good sources of fiber and other nutrients.
- Fortified Foods: Fortified cereals, milk, and other foods can help supplement protein intake, especially for those with limited access to diverse food sources.
- Lean Meats and Fish: Chicken, fish, and lean red meat are excellent sources of protein and iron.
It’s crucial to combine these foods in a balanced diet to ensure adequate protein intake and overall nutritional well-being.
Causes of Protein Deficiency in Indian Vegetarians
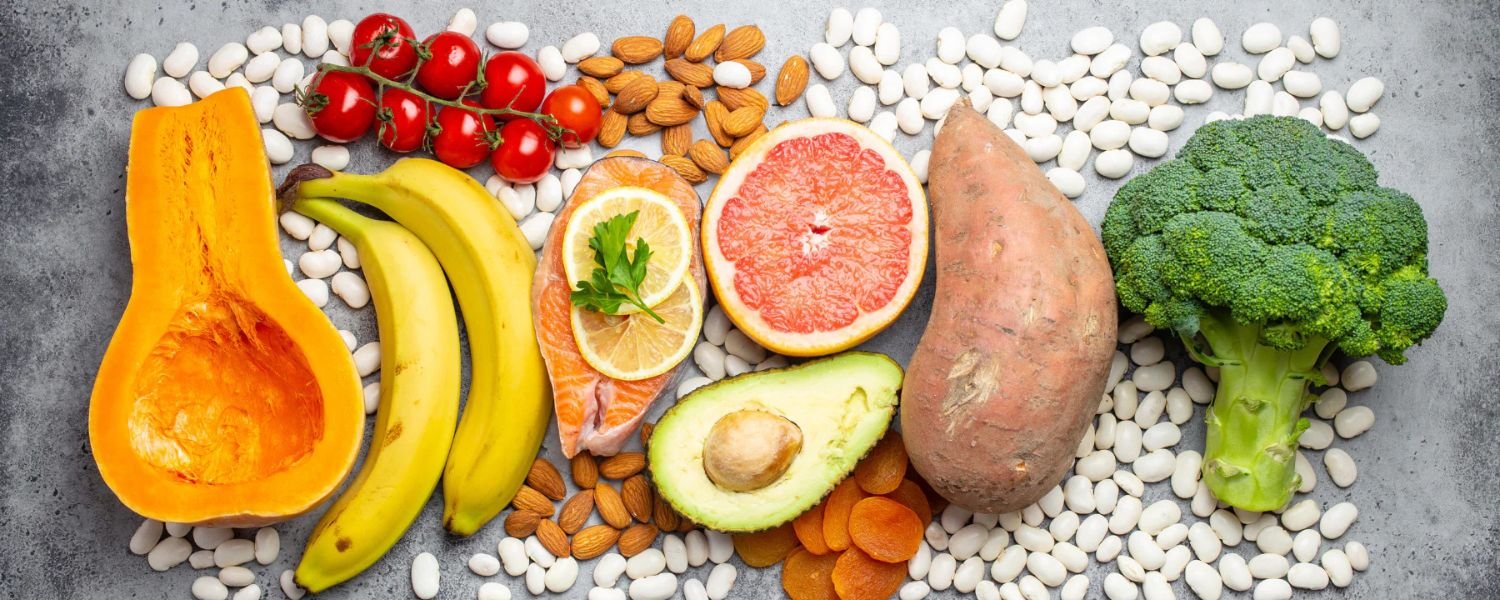

India has a significant vegetarian population, and while vegetarian diets can be healthy, they require careful planning to ensure adequate protein intake. Several factors contribute to protein deficiency among Indian vegetarians:
- Limited Access to Diverse Protein Sources: Many vegetarians rely heavily on grains and starchy vegetables, which are low in protein. Access to diverse protein sources like pulses, legumes, nuts, and seeds may be limited due to cost or availability.
- Lack of Awareness: Many vegetarians may not know the importance of combining different plant-based protein sources to ensure they get all the essential amino acids.
- Cultural Habits: Traditional Indian diets may not always prioritize protein intake, focusing more on carbohydrates.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty and food insecurity can limit access to protein-rich foods, especially for low-income vegetarian families.
- Improper Food Preparation: Some traditional cooking methods may reduce the bioavailability of protein in plant-based foods.
- Lack of Nutritional Education: Inadequate nutritional education can lead to poor dietary choices and insufficient protein intake.
- Reliance on single source of protein: Some vegetarians rely on single source of protein, which may not be enough to fulfill the daily protein requirement.
Health Consequences of Protein Deficiency

Protein deficiency can have a wide range of health consequences, affecting various systems in the body:
- Muscle Wasting: Protein is essential for building and maintaining muscle mass. Deficiency can lead to muscle wasting and weakness.
- Edema (Swelling): Protein helps maintain fluid balance. Deficiency can cause fluid to accumulate in tissues, leading to swelling, particularly in the abdomen and legs.
- Skin and Hair Problems: Protein is essential for healthy skin and hair. Deficiency can lead to dry, flaky skin, hair loss, and brittle nails.
- Weakened Immune System: Antibodies that fight off infections are made of protein. Deficiency weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Protein is essential for energy production. Deficiency can lead to fatigue, weakness, and decreased physical performance.
- Delayed Wound Healing: Protein is essential for tissue repair and regeneration. Deficiency can slow down wound healing.
- Anemia: Protein is necessary for the production of red blood cells. Deficiency can lead to anemia, characterized by fatigue, weakness, and pale skin.
- Cognitive Impairment: Protein is essential for brain development and function. Deficiency can lead to cognitive deficits, learning difficulties, and behavioral problems.
- Increased Risk of Fractures: Protein is essential for bone health. Deficiency can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures.
- Fatty Liver Disease: in severe cases, protein deficiency can cause fatty liver disease, as protein is needed to transport fats out of the liver.
Solutions for Protein Deficiency in Indian Vegetarians

Addressing protein deficiency in Indian vegetarians requires a multi-pronged approach:
Promoting Dietary Diversity:

Eat many plant foods like lentils, beans, nuts, and soy. This gives you all the building blocks your body needs. Mixing foods is like having a team, each food does a different job. A varied diet stops you from getting bored with food and helps your body get all the good things it needs.
Nutritional Education:

Learn why protein is important and how to combine plant foods. Understand how to put together meals that give you all the essential amino acids. Simple lessons can show you how to make tasty and healthy meals. Knowing what to eat helps you stay strong and healthy.
Food Fortification:

Add extra protein and vitamins to everyday foods like flour and rice. This ensures everyone gets important nutrients, even if they don’t eat many different foods. Fortified foods are an easy way to help everyone get the necessary nutrients, especially kids and older people.
Promoting Cultivation of Protein-Rich Crops:

Help farmers grow more beans and lentils. This makes them easier to find and cheaper to buy. More local crops means fresher food and stronger local economies. Growing these crops helps everyone have access to good protein sources.
Improving Access to Affordable Protein Sources:

Make sure everyone can buy healthy protein foods, especially poor families. Set up places to buy cheap, healthy food. This helps families eat well, even if they don’t have much money. Everyone deserves to have enough healthy food.
Promoting Awareness of Protein Requirements:

Teach people how much protein they need and how to get it from plants. Use simple ways to share this information. Understanding your body’s needs helps you make smart food choices. Knowing what your body needs allows you to stay healthy.
Promoting the use of sprouted pulses and fermented foods:
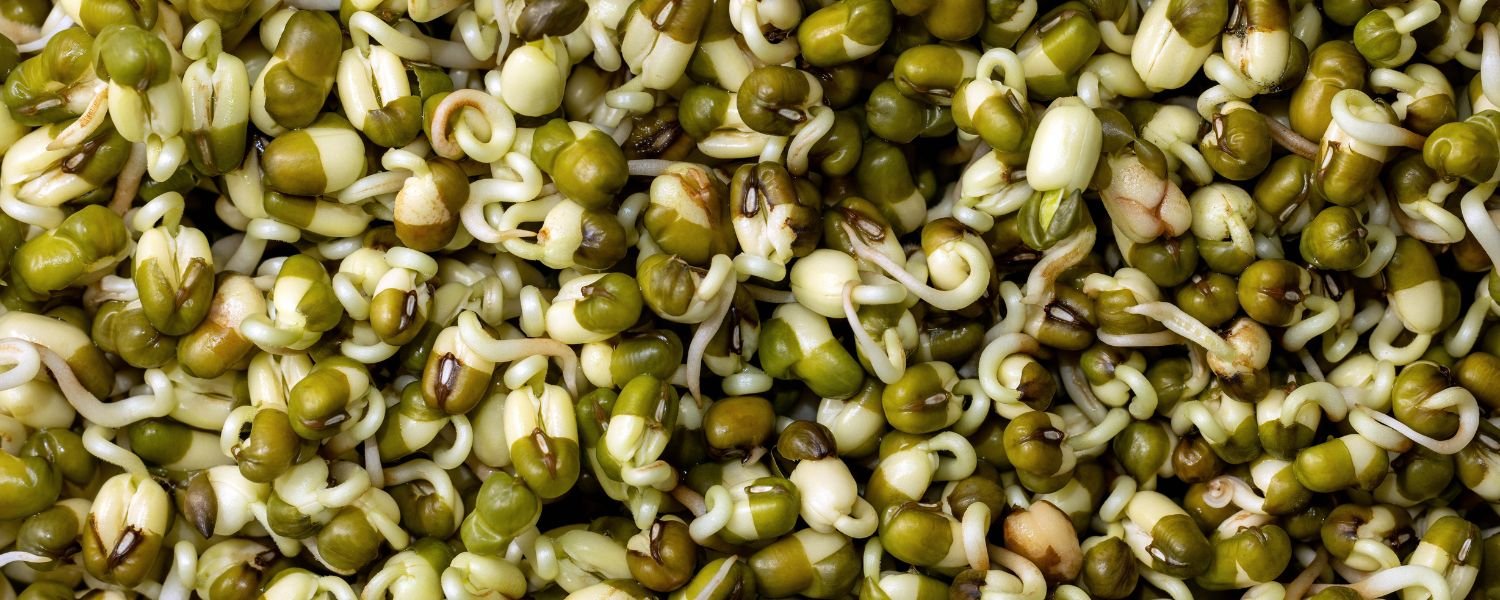

Show people how to sprout beans and make fermented foods. These methods make nutrients easier for your body to use. Using old ways of cooking can make food even healthier. These methods increase the amount of nutrients that your body can absorb.
Encouraging the use of protein supplements:
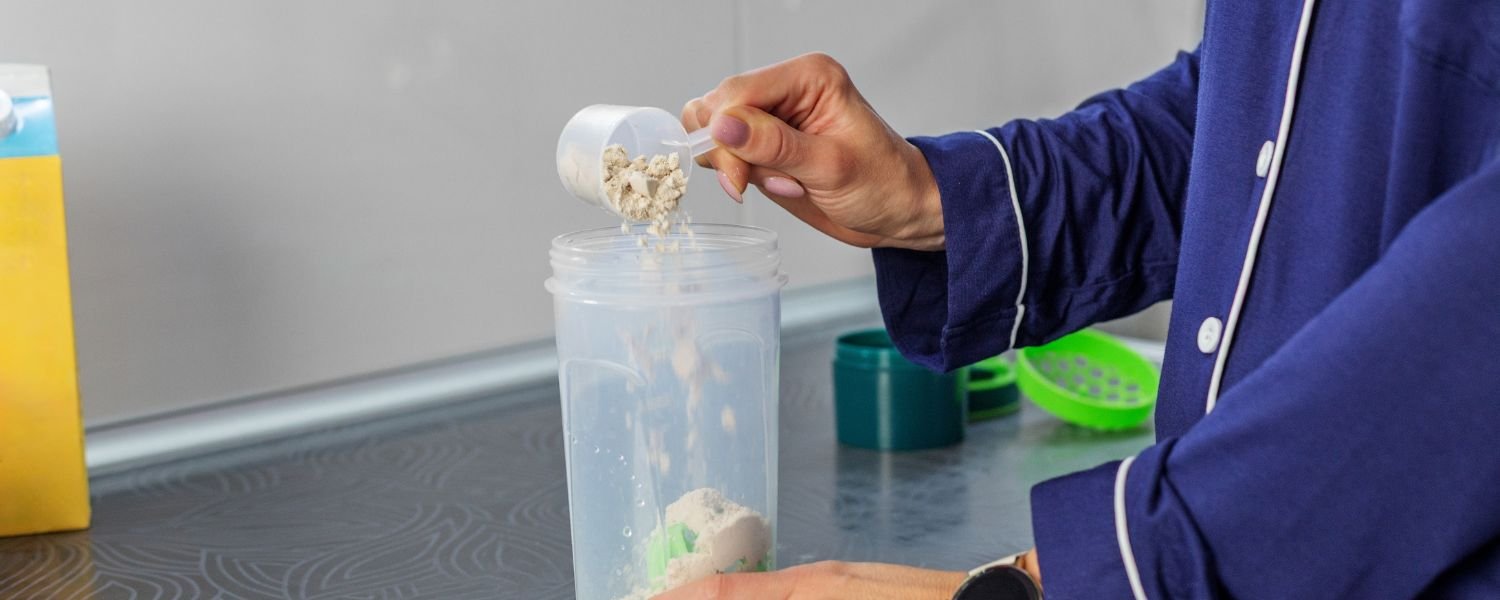

Use plant-based protein powders when people need extra protein. This helps people who are very sick or need a lot of protein. Supplements are a tool to help people who need more protein than they can get from food.
Addressing Socioeconomic Factors:

Help people get out of poverty and have enough food. This means helping people earn money and making sure they have food. When people have enough money and food, they can eat healthy. Helping people out of poverty improves their access to healthy foods.
Promoting sustainable agriculture:

Help farmers use ways to grow food that are good for the earth. This means having healthy soil and growing lots of crops for a long time. Healthy farming helps us have enough healthy food for everyone, now and in the future.
Focus on early intervention:

Give extra food and care to young children. This helps them grow strong and smart. Helping children early stops problems from happening later. Early intervention helps ensure a child can reach their full potential.
Regular health check-ups:

Give regular checkups and tests to find people with protein problems. Finding problems early means they can be fixed quickly. Regular checkups can help find issues before they become serious.
Promoting the consumption of traditional protein-rich foods:
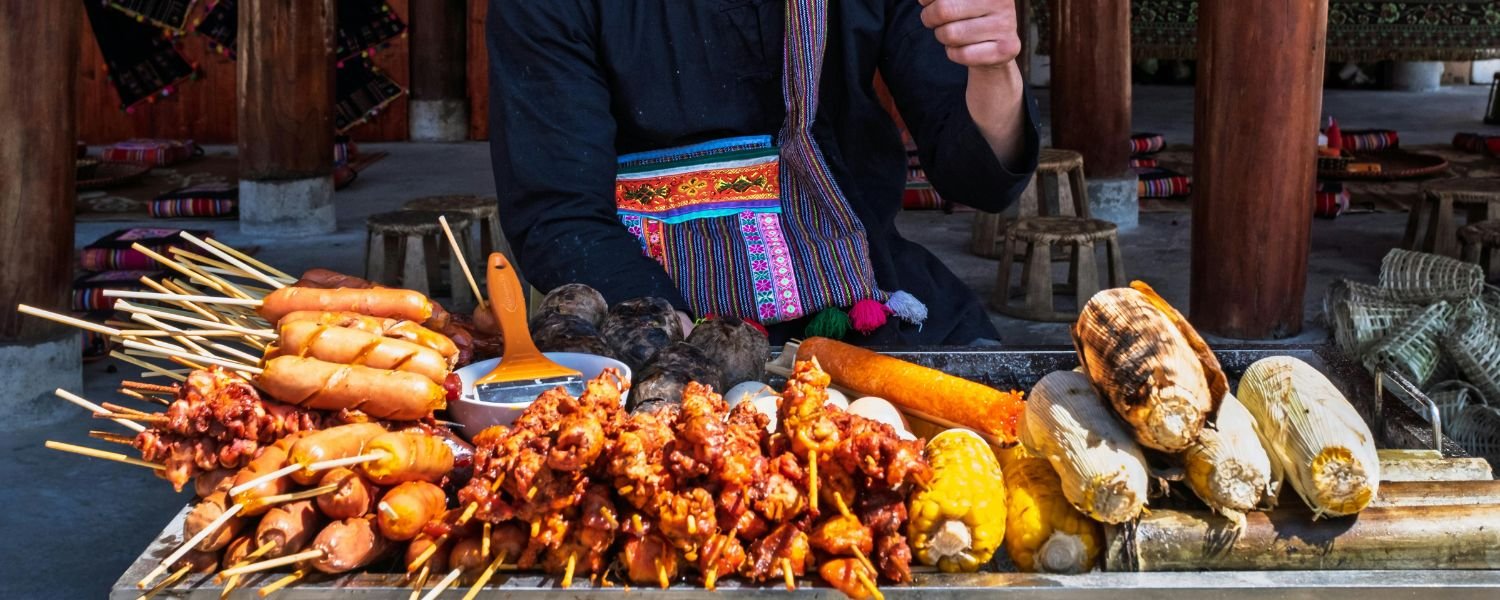

Encourage people to eat traditional Indian foods that are full of protein. Using foods that people already know and like makes it easier to eat healthy. Traditional foods are often designed to provide the body with the necessary nutrients.
Collaboration with NGOs and community leaders:

Work with local groups to help people in need. Local groups know their communities and can give help that works. Working together helps to reach more people and make a bigger difference.
Government initiatives:

Use government programs to help people get healthy food and care. Government programs can reach many people and make big changes. Government programs are essential to ensuring everyone has access to healthy food.
Using media to raise awareness:

Use TV, radio, and the internet to tell people about protein and healthy eating. Sharing information helps people make good choices. Using media helps to reach a large number of people with essential health information.
Conclusion
Protein deficiency in India is a significant public health issue, particularly among children and vegetarians.
Addressing this challenge requires a comprehensive approach that includes promoting dietary diversity, providing nutritional education, improving access to affordable protein sources, and addressing socioeconomic factors.
By implementing these solutions, India can improve the nutritional status of its population and ensure a healthier future for all.
Raising awareness of protein deficiency symptoms and causes and providing access to protein deficiency tests are also essential for early detection and intervention.
Through collaborative efforts and sustained commitment, they can overcome the challenge of protein deficiency in India and build a healthier, more prosperous nation.
To get more health related information follow us!