Odisha, a state located on the eastern coast of India, boasts a rich and diverse history that spans from ancient times to the modern era.
This historical journey reveals a land shaped by kingdoms, wars, cultural evolution, and modernization.
The story of Odisha is marked by its strategic location along the Bay of Bengal, which facilitated Maritime History of Odisha trade and cultural exchanges with various civilizations.
In this exploration, we’ll uncover the history of Odisha, tracing its evolution from ancient kingdoms to its modern-day identity.
The Artistic Legacy in the History of Odisha
1. History of Odisha
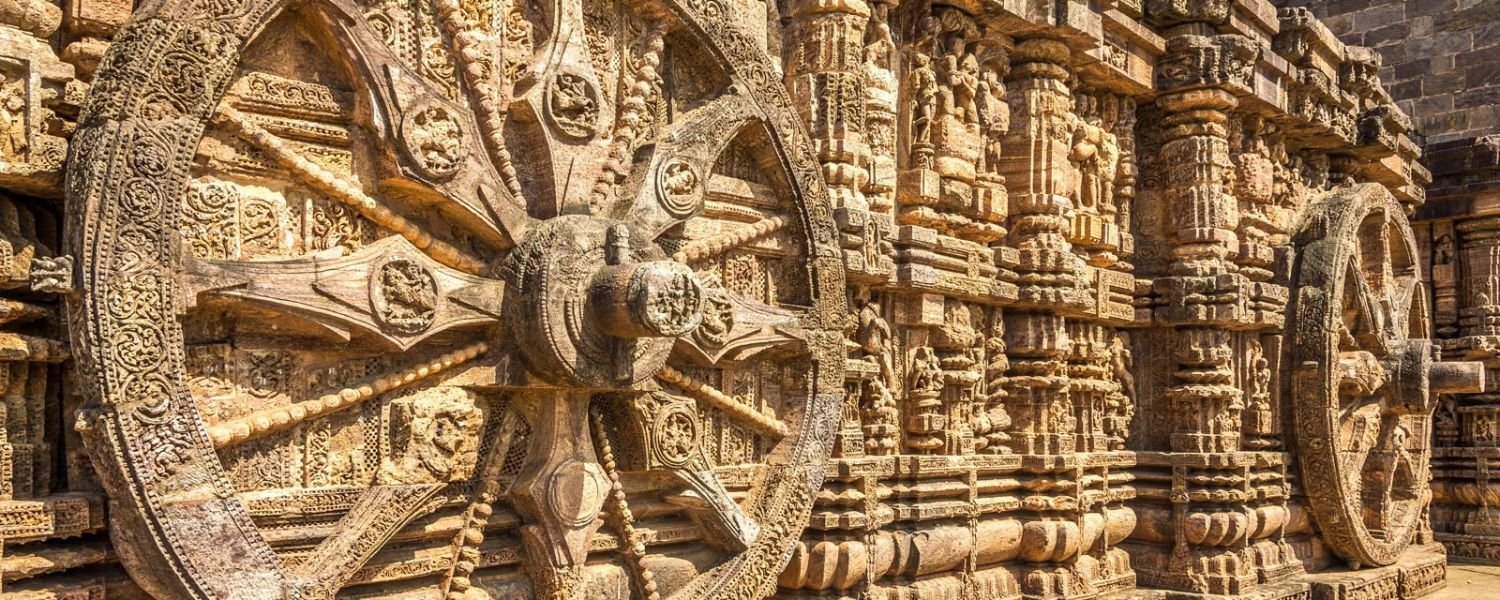

The history of Odisha is a tapestry woven with tales of grandeur, resilience, and transformation.
The state’s historical journey is marked by its early beginnings, flourishing kingdoms, cultural contributions, and adaptations to the modern world.
To understand this evolution, we delve into the ancient, medieval, and modern phases of Odisha’s history, while also exploring its art, architecture, and cultural heritage.
2. Historical Names of Odisha
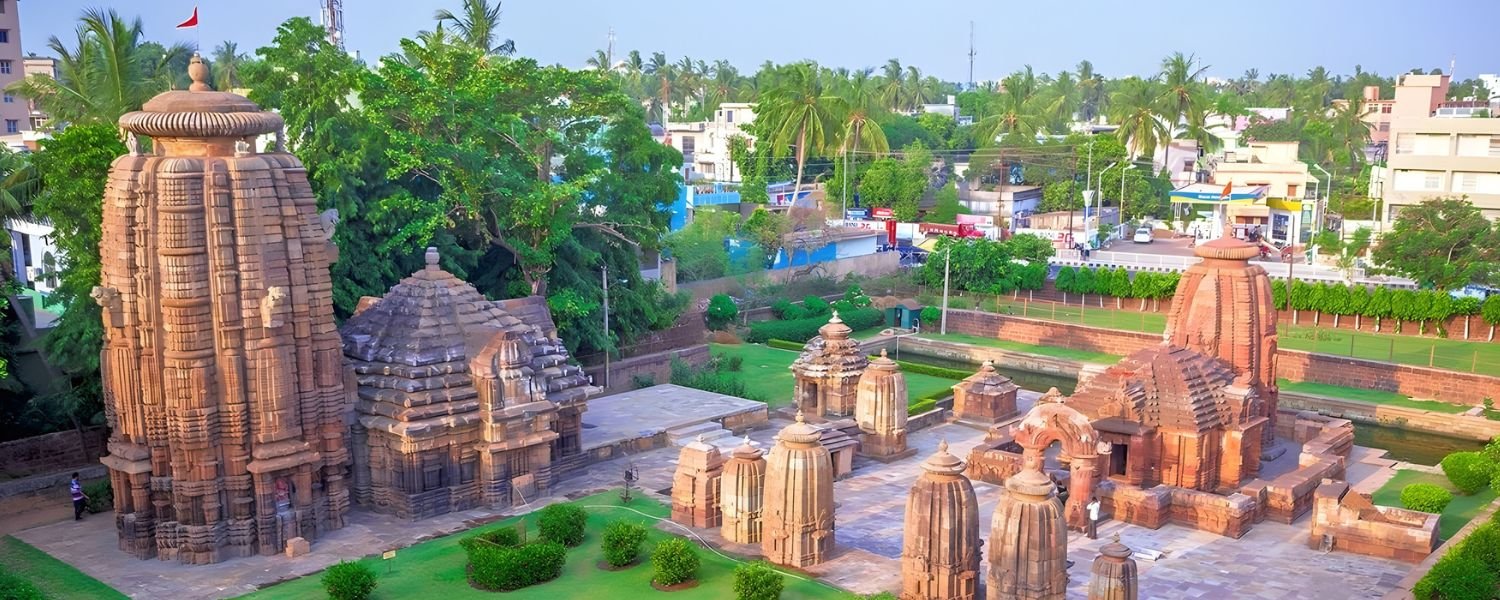

Odisha has been known by several names throughout its history. In ancient times, it was referred to as Kalinga, a name that is famously associated with the Kalinga War fought by Emperor Ashoka.
Other historical names include Utkala and Odra. Each name reflects different periods and cultural influences in the region’s history.
A. Prehistory

The prehistory of Odisha is characterized by evidence of early human settlements and their lifestyle.
Archaeological findings, such as tools, pottery, and cave paintings, suggest that the region was inhabited by early humans who engaged in hunting, gathering, and rudimentary agriculture.
The prehistorical period set the foundation for the development of more complex societies in Odisha.
Additionally, the Rivers of India played a crucial role in shaping the region’s culture and economy, providing essential resources for these early communities.
B. Ancient Odisha
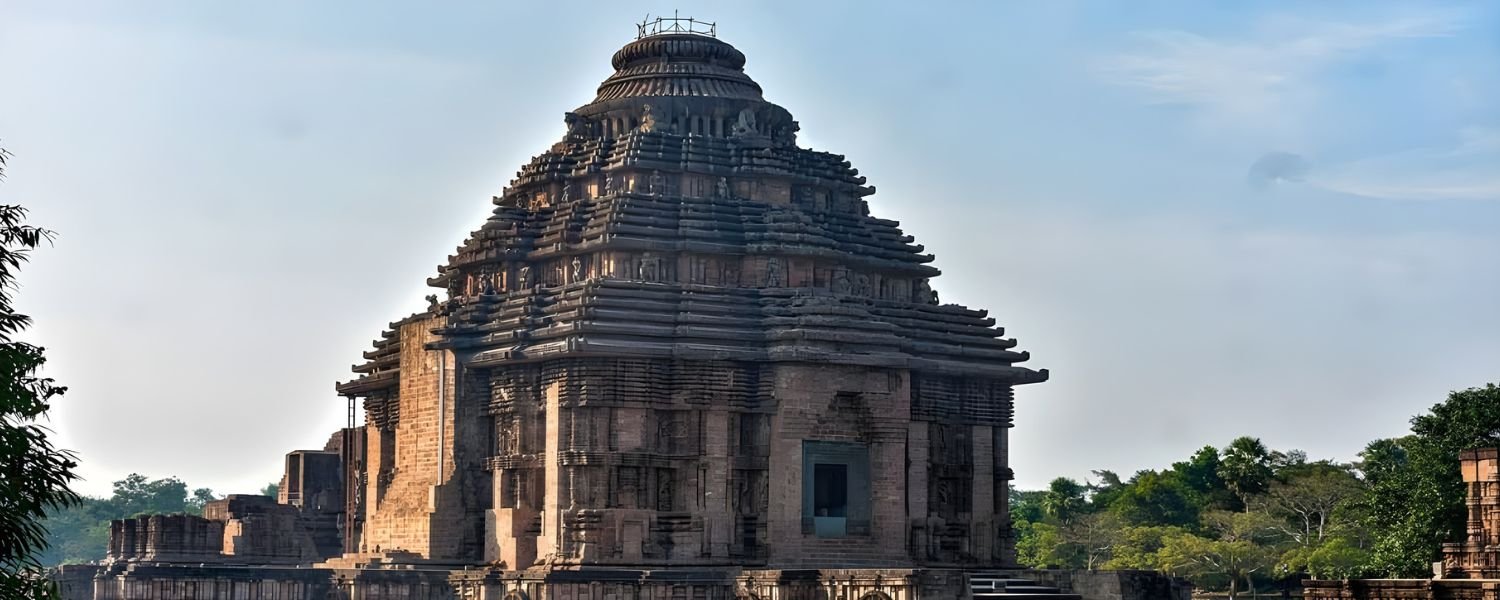

Ancient Odisha is marked by the rise of significant kingdoms and dynasties. The most notable of these was the Kalinga Kingdom, renowned for its rich cultural and historical legacy.
The Kalinga War in 261 BCE, fought between the Mauryan Empire under Ashoka and the Kalinga History of Odisha, is a pivotal event in ancient Odisha’s history.
This war not only altered the political landscape but also had profound cultural and historical implications.
The Mauryan Empire’s influence brought about a period of prosperity and cultural exchange.
Following the Mauryan era, Odisha saw the rise of several local dynasties, including the Somavamsa and Ganga dynasties, which contributed to the region’s political stability and cultural development.
C. Medieval Odisha
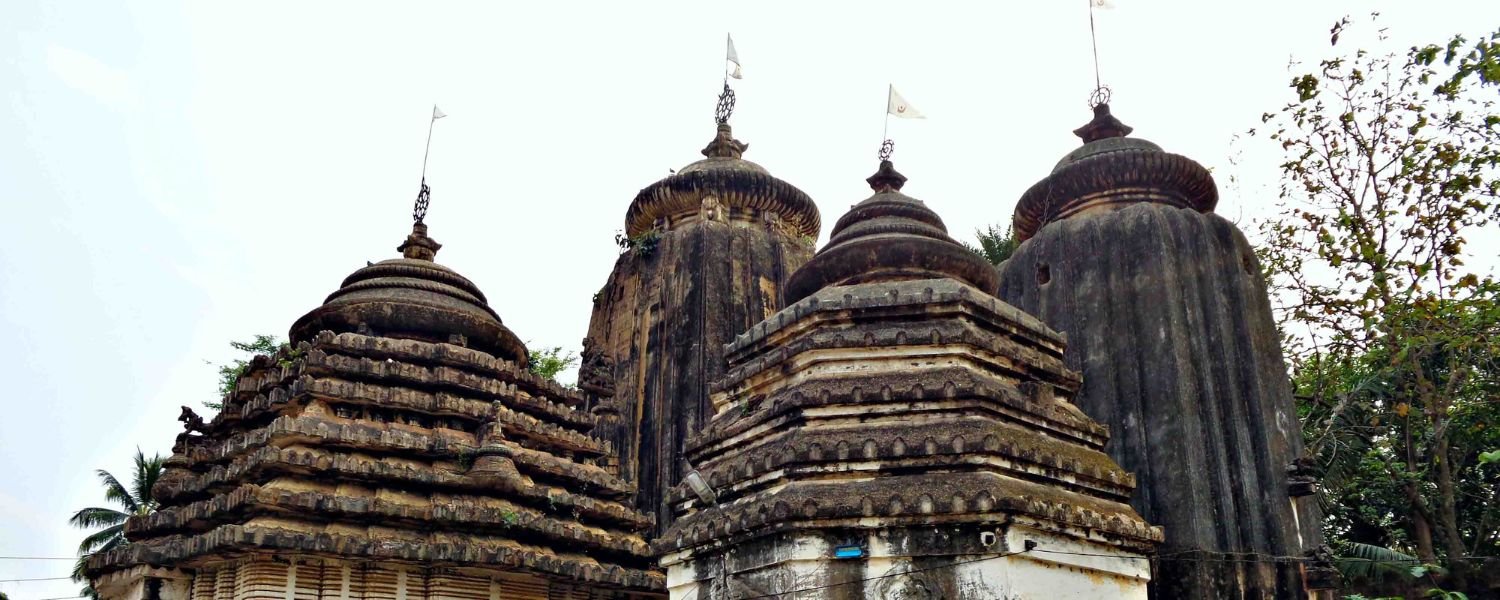

The medieval period in Odisha saw the rise of several powerful dynasties, including the Ganga dynasty and the Suryavamsa dynasty.
During this time, Odisha experienced significant political and cultural developments.
The Ganga dynasty, in particular, made significant contributions to architecture and art, including the construction of the famous Lingaraj Temple in Bhubaneswar.
The medieval era also saw the flourishing of trade and commerce, with Odisha becoming an important center for maritime trade.
The state’s strategic location along the Bay of Bengal facilitated interactions with various civilizations, including Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
D. Modern Era

The modern era in Odisha features significant socio-political changes. During the British colonial period, the British incorporated Odisha into the Bengal Presidency, and it later became a separate state in independent India.
The struggle for Odia nationalism played a crucial role in shaping the modern identity of Odisha.
The efforts of leaders like Utkal Gourab Madhusree and others were instrumental in promoting Odia language and culture.
Post-independence, Odisha has undergone significant development in various sectors, including infrastructure, education, and industry.
The state has also faced challenges, such as natural disasters and economic disparities, but has made strides towards modernization and progress.
3. Architecture of Odisha

The architecture of Odisha is renowned for its grandeur and intricacy. The state is home to some of the most exquisite temples and monuments in India.
The temples of Odisha are known for their distinctive architectural style, characterized by intricate carvings, towering spires, and beautifully sculpted deities.
One of the most iconic examples of Odisha’s architecture is the Jagannath Temple in Puri, which is a major pilgrimage site and an architectural marvel.
Other notable temples include the Lingaraj Temple and the Sun Temple at Konark, both of which showcase the architectural brilliance of ancient Odisha.
4. Art and Culture in Odisha
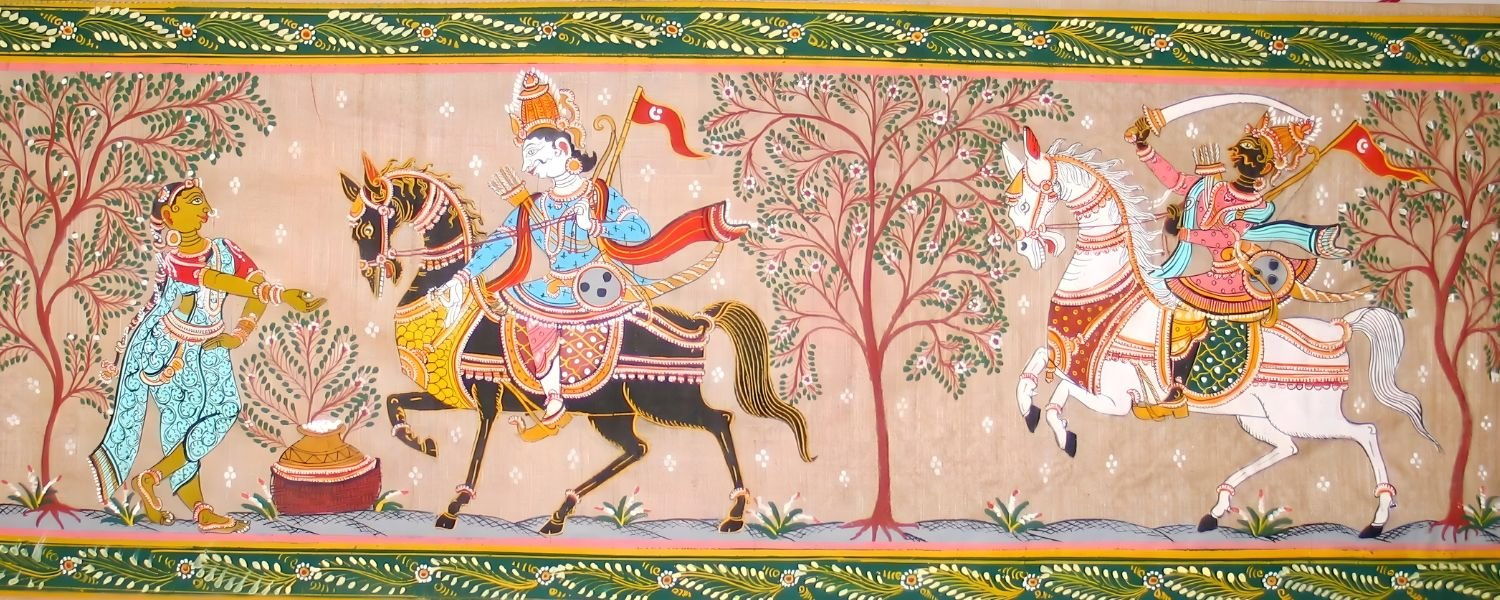

Odisha’s art and culture are deeply rooted in its historical and religious traditions. The state is known for its Festivals of Odisha, traditional dance forms, and artistic expressions.
The cultural heritage of Odisha reflects a blend of historical influences and local traditions.
5. Temples of Odisha
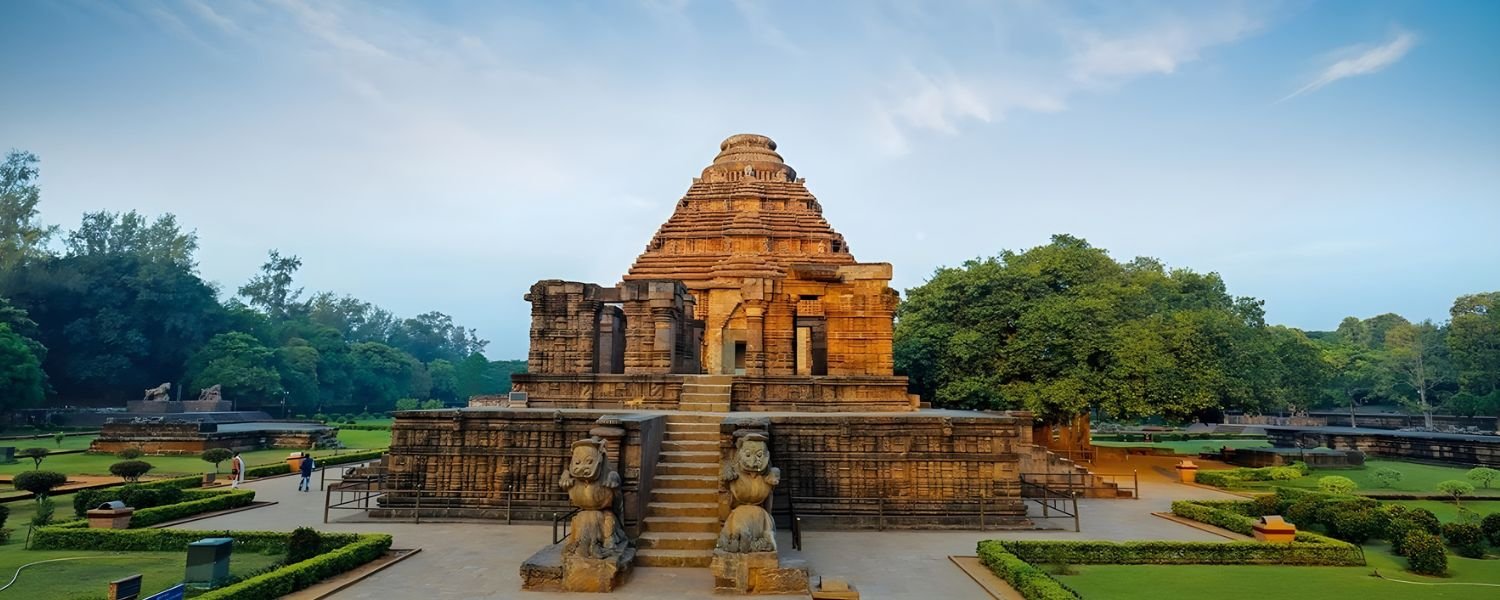

The temples of Odisha are not only architectural masterpieces but also centers of spiritual and cultural significance.
The Jagannath Temple in Puri stands out as one of the most famous temples, known for its annual Rath Yatra, a grand chariot festival that attracts millions of devotees.
The Konark Sun Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, boasts intricate carvings and a unique design that depict the chariot of the Sun God.
6. Odissi Dance
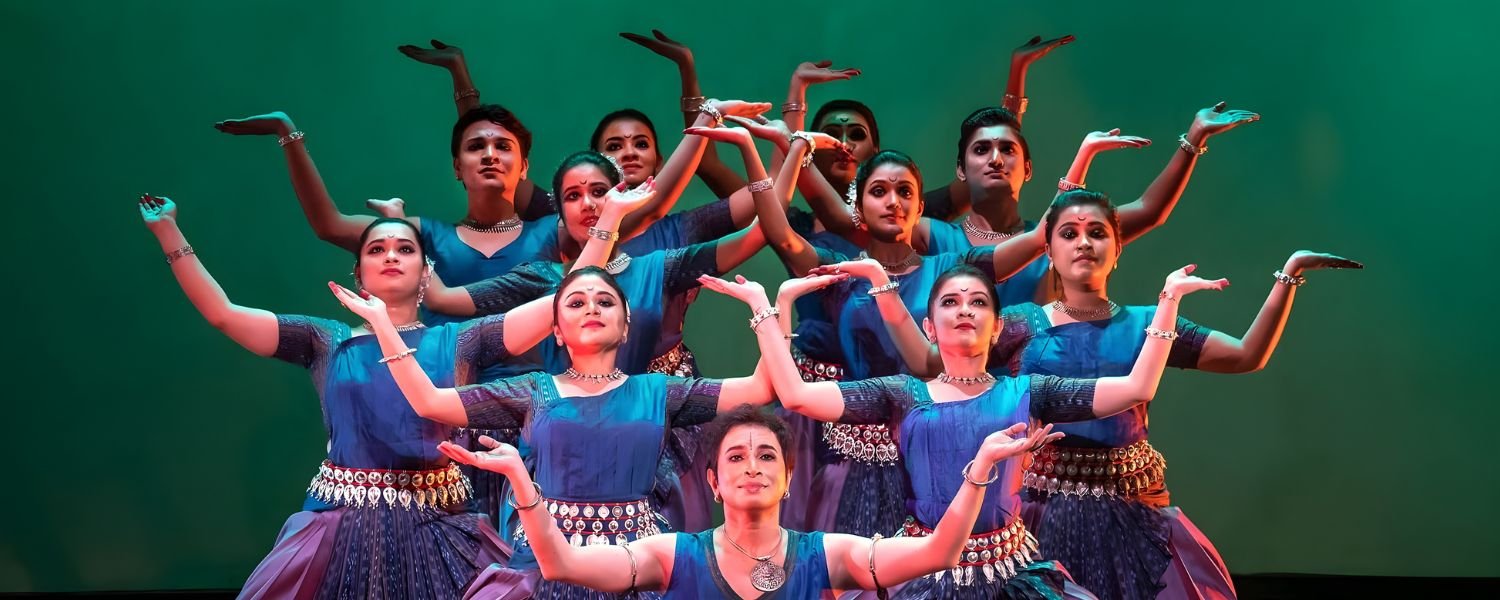
Odissi dance is one of the classical dance forms of India that originated in Odisha. This dance form features graceful movements, expressive gestures, and intricate footwork.
Odissi dance has ancient roots and connects deeply to the temple rituals and cultural practices of Odisha.
Performers present it as both a solo and group dance, showcasing the rich artistic heritage of the state.
7. Festivals of Odisha
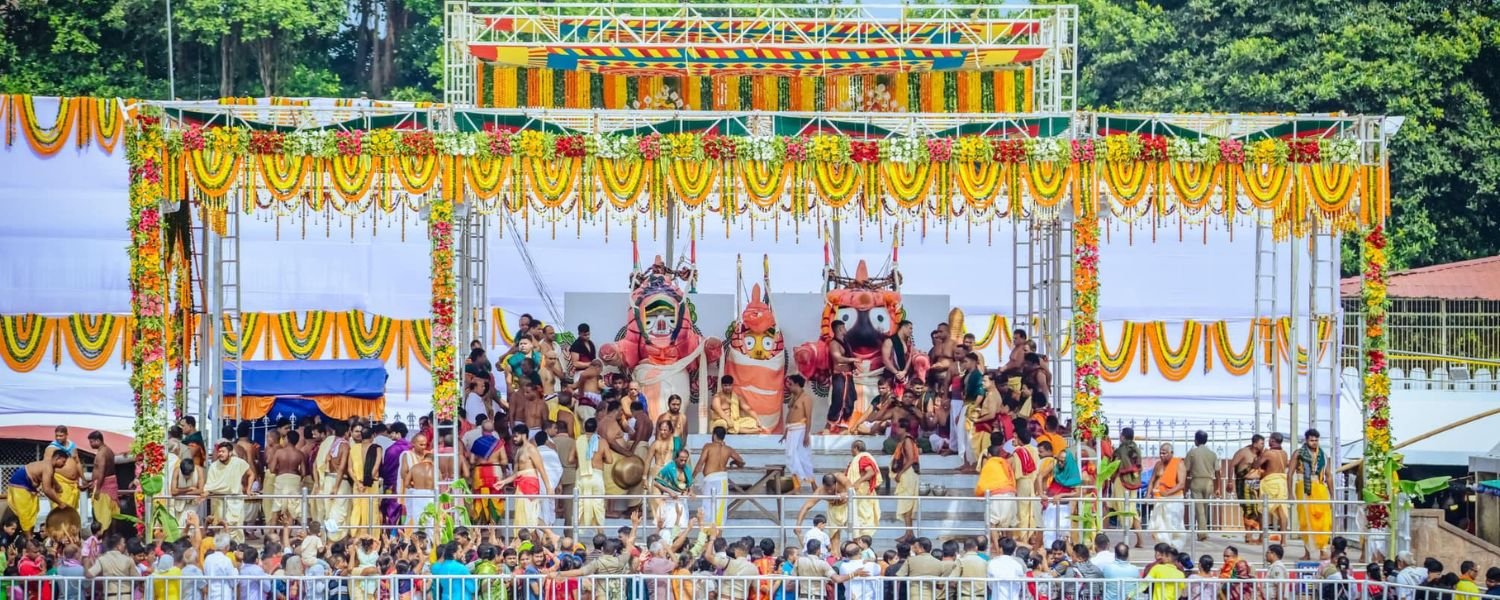

Odisha celebrates a variety of festivals that reflect its cultural diversity and religious traditions. Major festivals include:
A. Rath Yatra
The grand chariot festival held in Puri, celebrating Lord Jagannath.
B. Durga Puja
A major festival dedicated to the goddess Durga, celebrated with elaborate decorations and rituals.
C. Diwali
The festival of lights, marked by festivities and cultural events.
D. Saraswati Puja
Celebrated in honor of the goddess Saraswati, known for wisdom and learning.
These festivals bring communities together and showcase the vibrant cultural heritage of Odisha.
8. Foods of Odisha
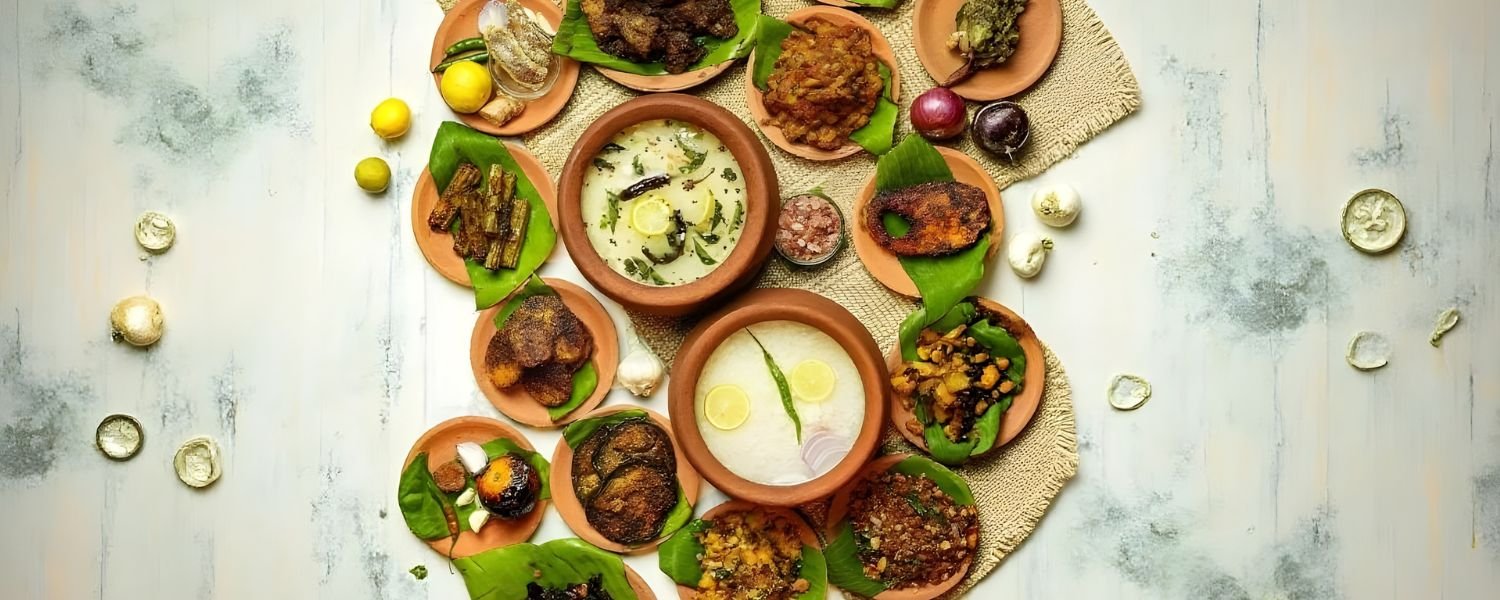

The cuisine of Odisha is known for its distinctive flavors and ingredients. Some popular dishes include:
A. Pakhala Bhata
Fermented rice served with vegetables and yogurt.
B. Dalma
A hearty lentil and vegetable stew.
C. Rasgulla
Afamous sweet made from chenna (cottage cheese) and sugar syrup.
D. Chenna Poda
A baked dessert made from chenna and sugar, often enjoyed as a sweet treat.
Odisha’s cuisine reflects its rich cultural traditions and diverse influences, offering a unique culinary experience.
Conclusion
The history of Odisha is a rich and fascinating journey that spans from ancient times to the present day.
From its early beginnings as Kalinga to its role in modern India, Odisha has been a land of cultural, political, and artistic significance.
The state’s ancient history of Odisha, medieval history of Odisha, and modern history of Odisha highlight its evolution and resilience.
The architecture of Odisha, including its temples and monuments, stands as a testament to the artistic and architectural achievements of its people.
The state’s art and culture, including Odissi dance, festivals, and cuisine, reflect its vibrant and diverse heritage.
As Odisha continues to embrace modernization while preserving its rich cultural legacy, it remains a land of historical significance and cultural splendor.
The story of Odisha is a testament to its enduring spirit and its contributions to the broader tapestry of Indian history and culture.
FAQ
Q1. What is the historical significance of Odisha?
A. Odisha, formerly known as Kalinga, has a rich history marked by significant events such as the Kalinga War, which led to Emperor Ashoka’s conversion to Buddhism. The region has been a center of culture, trade, and art, significantly contributing to Indian history through its ancient kingdoms, medieval dynasties, and modern developments.
Q2. What were the ancient names of Odisha?
A. Odisha has several names throughout history, including Kalinga, Utkala, and Odra. Each name reflects different periods and cultural influences in the region’s history.
Q3. What was the impact of the Kalinga War on Odisha’s history?
A. The Kalinga War, fought in 261 BCE between Emperor Ashoka of the Mauryan Empire and the Kalinga rulers, had a profound impact on Odisha. The war’s devastation led Ashoka to embrace Buddhism and promote peace, influencing both regional and global perspectives on the importance of non-violence.
Q4. What are some notable temples in Odisha?
A. Odisha boasts renowned temples, including the Jagannath Temple in Puri, celebrated for the annual Rath Yatra festival, and the Konark Sun Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site famous for its architectural grandeur and intricate carvings. The Lingaraj Temple in Bhubaneswar is another significant temple reflecting the state’s architectural brilliance.
Q5. What is Odissi dance, and what is its significance?
A. Odissi dance is a classical dance form originating in Odisha. The graceful movements, expressive gestures, and intricate footwork characterize this dance form. Deeply rooted in the temple traditions of Odisha, performers showcase the region’s rich artistic heritage through both solo and group dances.
Q6. How did Odisha contribute to Indian maritime history?
A. Odisha has a significant maritime history due to its strategic location along the Bay of Bengal. The state was an important center for maritime trade, facilitating exchanges with civilizations in Southeast Asia and the Middle East. This trade contributed to the economic and cultural development of the region.