DIY hydroponic systems have emerged as a beacon of innovation in sustainable agriculture, offering a revolutionary approach to growing plants without soil.
This method conserves water and maximises space utilisation, making it a solution for urban gardening enthusiasts and aspiring farmers.
With the focus on self-sufficiency and environmental consciousness intensifying, DIY hydroponic systems have gained immense popularity among individuals seeking to cultivate fresh produce in their homes or small-scale farms.
DIY hydroponic systems deliver essential nutrients directly to the plant’s roots, suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution.
By eliminating the need for soil, growers can avoid common challenges such as pests, diseases, and limited space, thereby enhancing crop yields and quality.
This approach offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing enthusiasts to customise their systems based on available resources and personal preferences.
The beauty of DIY hydroponic systems lies in their accessibility and adaptability.
Utilising readily available materials such as PVC pipes, plastic containers, or even recycled materials, enthusiasts can construct their hydroponic setups at a fraction of the cost of commercial systems.
This affordability, coupled with the satisfaction of building something from scratch, adds to the allure of DIY hydroponics.
1. Kratky Method

The Kratky Method is a popular DIY hydroponic system that allows plants to grow without needing electricity, pumps, or complex equipment.
Dr. Bernard Kratky, a researcher, developed this method at the University of Hawaii, and it is ideal for beginners or those with limited space and resources.
The Kratky Method involves growing plants in containers filled with a nutrient solution, with the plant roots suspended in the solution without any aeration or circulation.
As the plant grows, the nutrients from the water level gradually decrease.
Unlike traditional hydroponic systems, which require constant monitoring and adjustment of nutrient levels and water circulation, the Kratky Method is passive and automated.
The container is filled with enough nutrient solution to last the growing period, and no additional water or nutrients are added.
This makes it a low-maintenance and cost-effective option for growing various types of plants, including leafy greens, herbs, and some fruiting crops.
The Kratky Method has gained popularity among home gardeners and urban farmers looking for simple and sustainable ways to grow their food.
2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
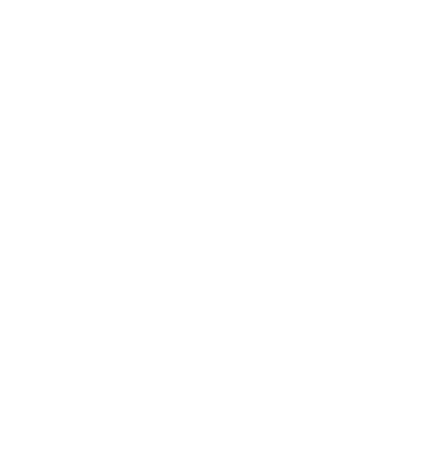
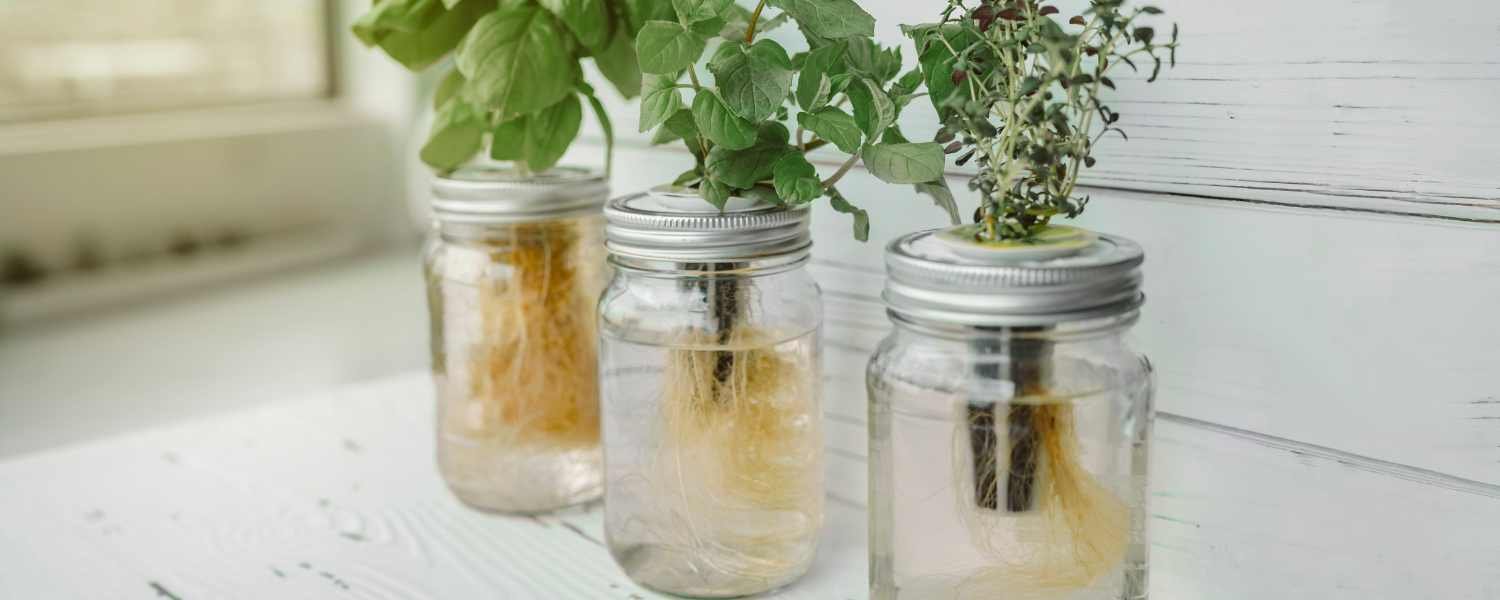
Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a popular method used in DIY hydroponic systems for growing plants without soil.
In DWC, plants are suspended in a rich nutrient solution and continuously aerated to provide oxygen to the roots.
The roots of the plants dangle freely in the nutrient solution, allowing them to absorb water and nutrients directly.
To set up a DWC system, a container or reservoir is filled with the nutrient solution, and a floating platform or net pot is used to support the plants above the solution.
An air pump and airstone are then used to oxygenate the nutrient solution, ensuring the roots have access to oxygen.
DWCs are easy to set up and maintain, making them a popular choice for DIY hydroponic enthusiasts.
They are particularly well-suited for growing leafy greens and herbs, although they can also be used to produce a variety of other plants.
Overall, Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a simple and effective method for growing plants hydroponically, allowing for efficient nutrient uptake and rapid growth.
3. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
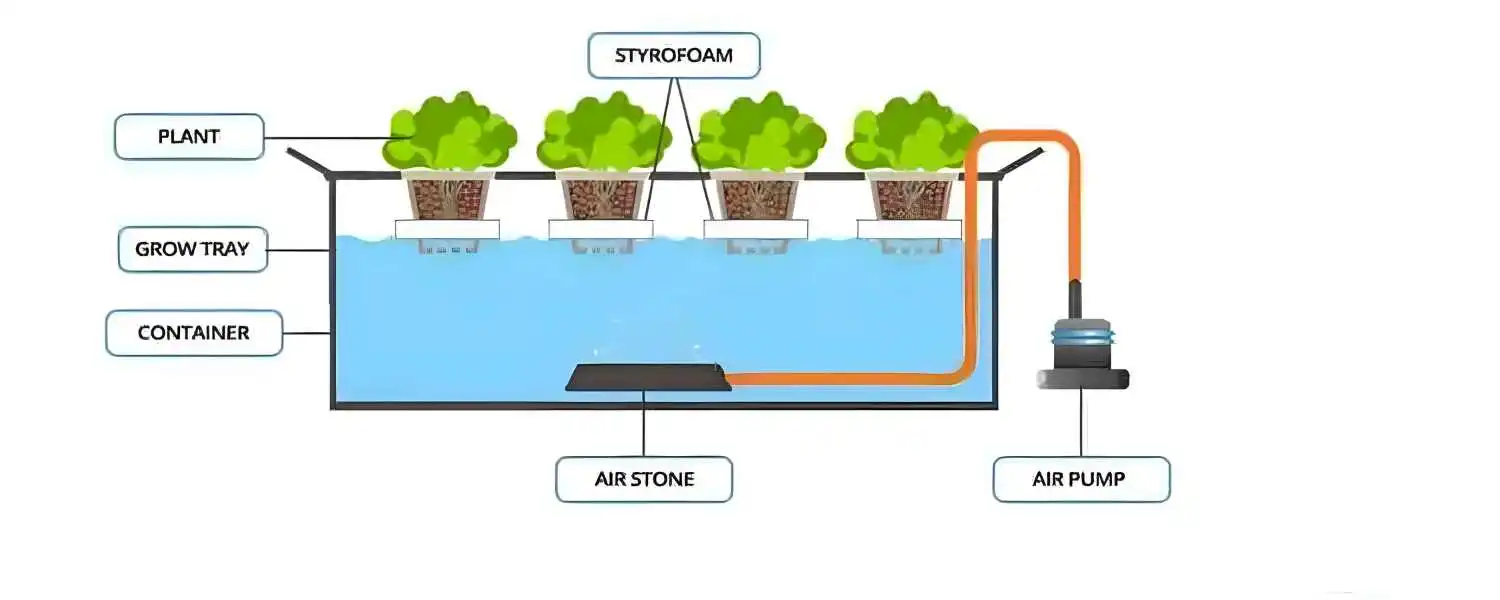
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is a popular method used in DIY hydroponic systems to grow plants without soil.
In NFT systems, plants are placed in small cups or baskets and suspended in channels or gutters, allowing their roots to be continuously exposed to a thin film of nutrient-rich water.
The channels are typically sloped to allow the nutrient solution to flow gently over the roots, providing them with the essential nutrients they need for growth.
The roots take the nutrients directly from the water, while the excess solution is recirculated back to the reservoir for reuse.
NFT systems are known for their simplicity and efficiency, requiring less water and nutrients than traditional soil-based gardening.
They also allow for better control over plant nutrition and growth, resulting in healthier and more productive crops.
NFT systems are great for growing leafy greens, herbs, and small plants with shallow roots.
Additionally, they can be scaled to accommodate different space constraints and plant requirements.
Overall, the Nutrient Film Technique offers a cost-effective and space-efficient solution for DIY hydroponic gardening, allowing anyone to grow fresh and nutritious produce at home.
4. Wick System
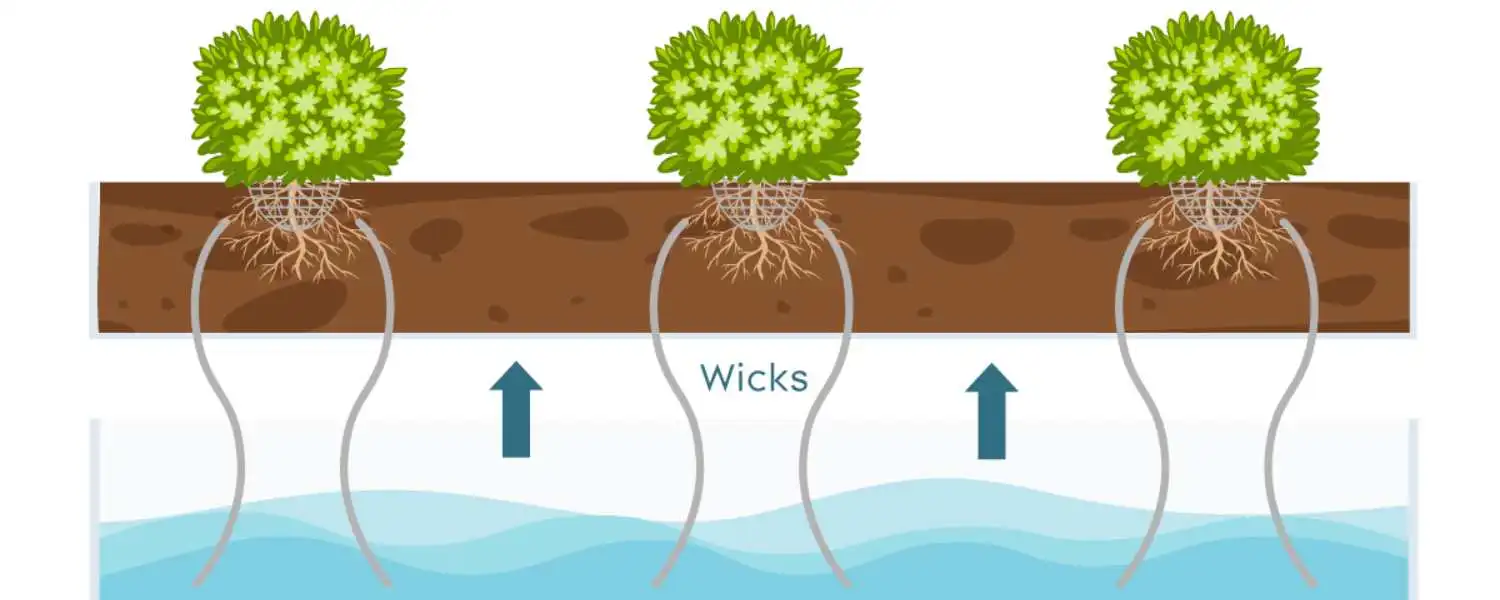
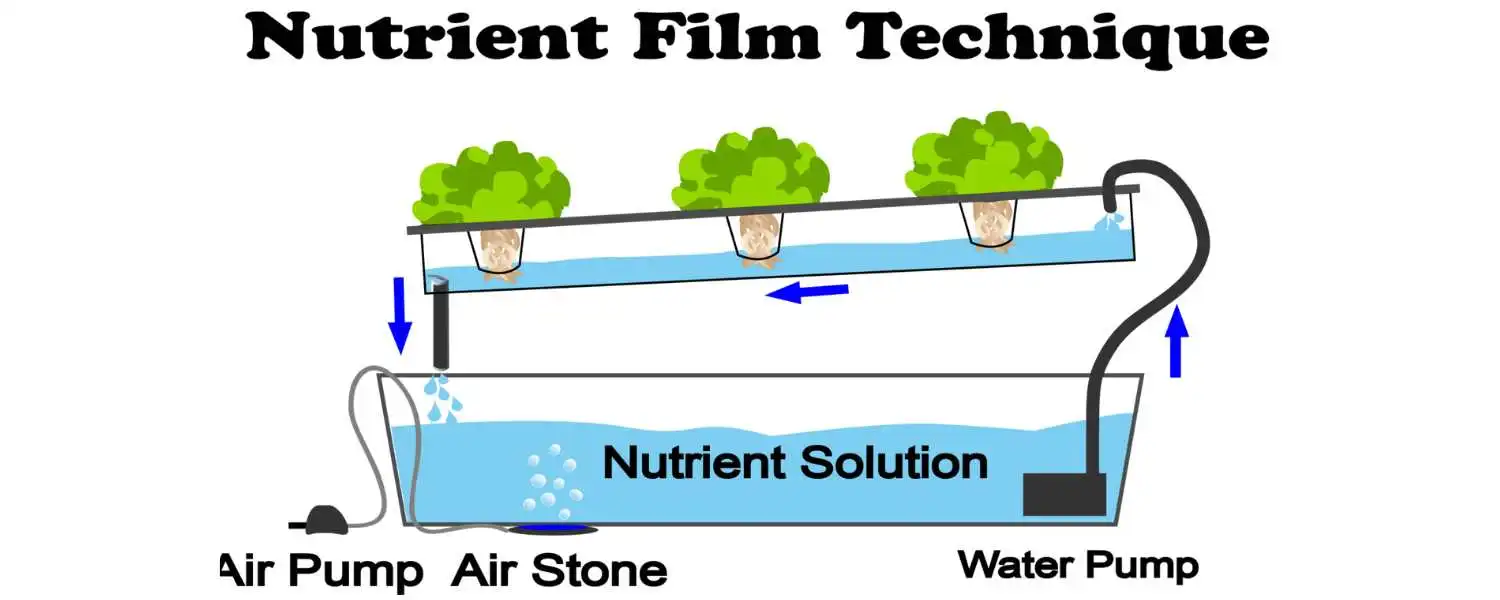
The wick system is one of the most straightforward and beginner-friendly DIY hydroponic systems available.
It requires minimal equipment and is easy to set up at home.
In a wick system, plants are grown in a container filled with a growing medium, like perlite or coconut coir, supporting the roots.
A wick, typically made of cotton or felt, is the plant stem inserted into a growing medium with roots in a nutrient solution reservoir below.
The wick acts as a conduit, drawing up the nutrient solution from the reservoir and sending it directly to the roots of the plants.
This passive nutrient delivery method eliminates the need for pumps or electricity, making the wick system low-cost and energy-efficient. However, ensuring that the wick is made of a porous material that can effectively transport the nutrient solution to the plant’s roots is essential.
Additionally, the wick system may not be suitable for large or heavy plants, as the wick may need help to provide adequate nutrient uptake.
Overall, the wick system is a simple and effective option for beginners exploring DIY hydroponics at home.
5. Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
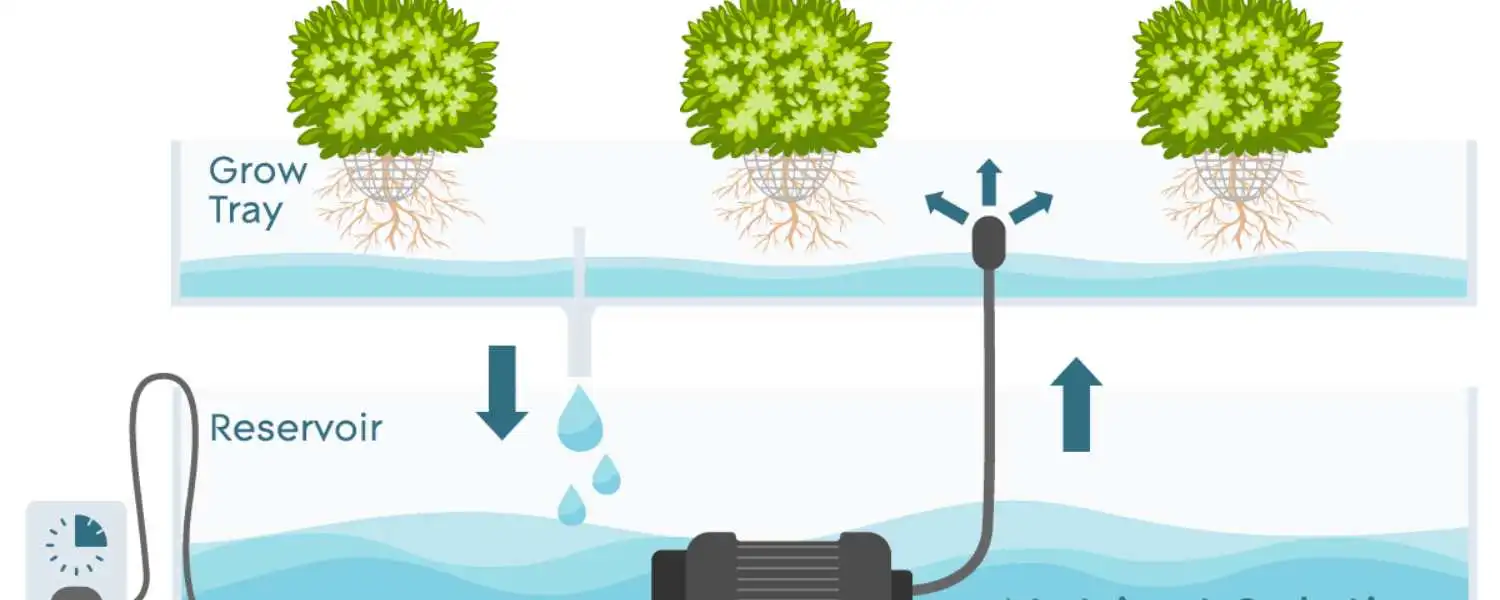
Ebb/Flow, or Flood and Drain, is a popular method for growing plants in DIY hydroponic systems.
In this system, plants are grown in some items filled with a growing medium, such as perlite or clay pellets.
A nutrient solution is periodically pumped into the containers, flooding the increasing medium and providing the plants with essential nutrients.
Once the containers are attacked, the excess nutrient solution can drain back into a reservoir, leaving the roots with access to oxygen.
This cycle of flooding and draining is controlled by a timer, which ensures that the plants receive the right amount of water and nutrients at regular intervals.
Ebb and Flow systems are relatively easy to set up and maintain, making them popular among beginner hydroponic enthusiasts.
They can be customised to fit various plant sizes and types, making them suitable for different crops.
Additionally, Ebb and Flow systems can be automated using pumps and timers, allowing for more efficient and consistent nutrient delivery.
Overall, Ebb and Flow systems offer a simple yet effective solution for growing plants hydroponically in a DIY setting.
6. Aeroponics
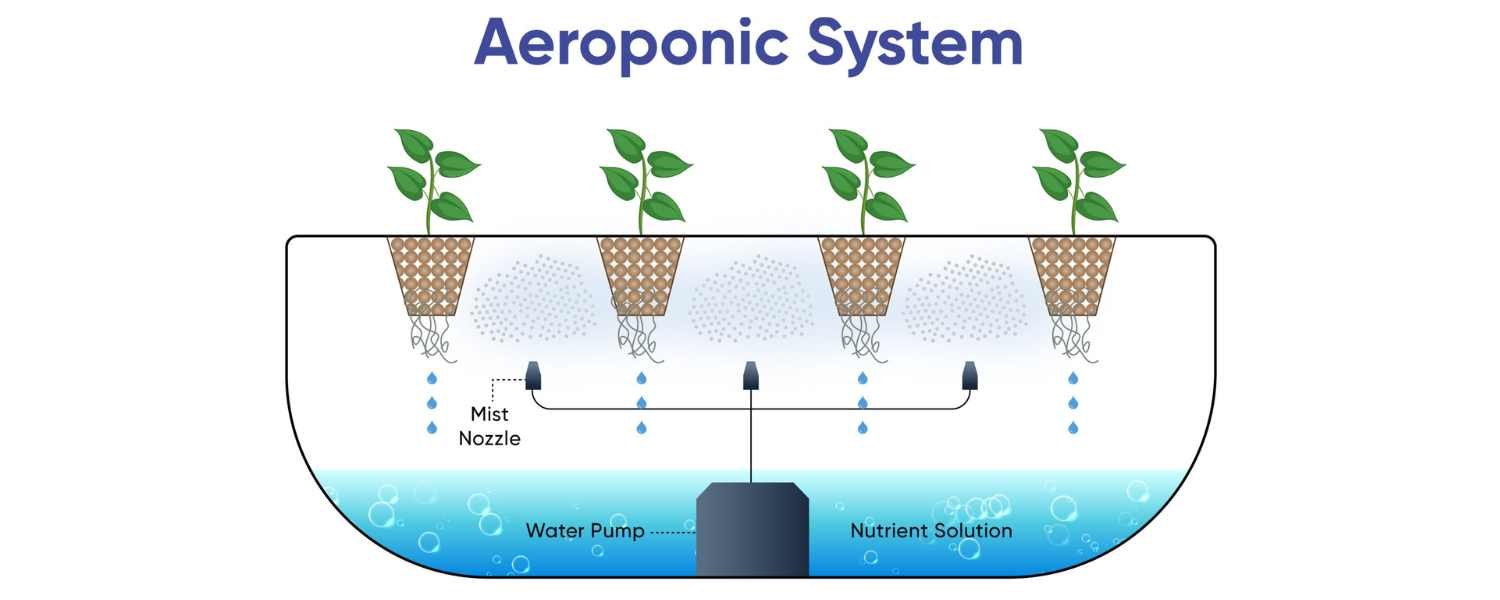
Aeroponics is a system of growing plant roots suspended in the air or misted with a nutrient-rich solution.
This technique allows plants to receive the nutrients they need directly through their roots while providing ample oxygen.
Aeroponics systems typically consist of a reservoir that holds the nutrient solution, a pump to deliver the solution to the roots, and misters or nozzles to create a fine mist around the roots.
DIY hydroponic systems are often used for aeroponic gardening, where individuals make their setups using readily available materials such as PVC pipes, plastic containers, and misting systems.
One main advantage of aeroponics is that it allows for plant growth and higher yields than traditional soil gardening.
Additionally, aeroponic systems use less water and require fewer nutrients, making them a more sustainable option for growing plants.
Aeroponics is also ideal for growing plants indoors or in limited space environments, as it does not require soil and can be easily customised to fit any space.
Overall, aeroponics is a versatile and efficient method of growing plants that offers numerous benefits for amateur and experienced gardeners.
7. Perlite and Vermiculite Systems
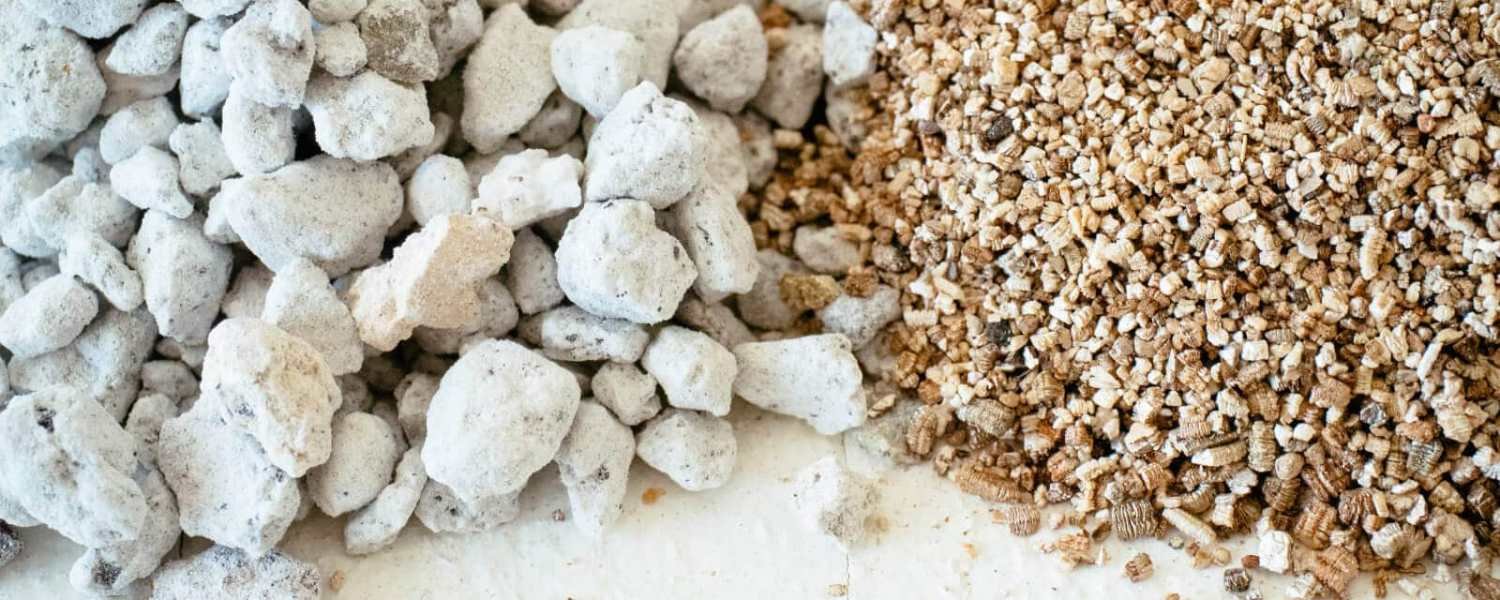

Perlite and vermiculite systems are commonly used in DIY hydroponic systems to provide support and aeration to plant roots.
Perlite is a lightweight volcanic rock heated until it expands, creating a porous material with excellent drainage properties.
In hydroponics, perlite is often used as a growing medium due to its ability to contain moisture while allowing water to drain away or preventing root rot and other issues issued by waterlogging.
Vermiculite, on the other hand, is a natural mineral that is heated to high temperatures, causing it to expand into a lightweight and absorbent material.
In hydroponics, vermiculite is used to improve moisture retention in the growing medium, ensuring that plant roots have access to water and nutrients at all times.
Both perlite and vermiculite systems are easy to use.
They can be incorporated into various DIY hydroponic setups, including deep water culture, nutrient film technique, and ebb and flow systems.
With proper care and maintenance, perlite and vermiculite systems can help home gardeners grow healthy and productive plants without needing soil.
8. Vertical Hydroponic Systems
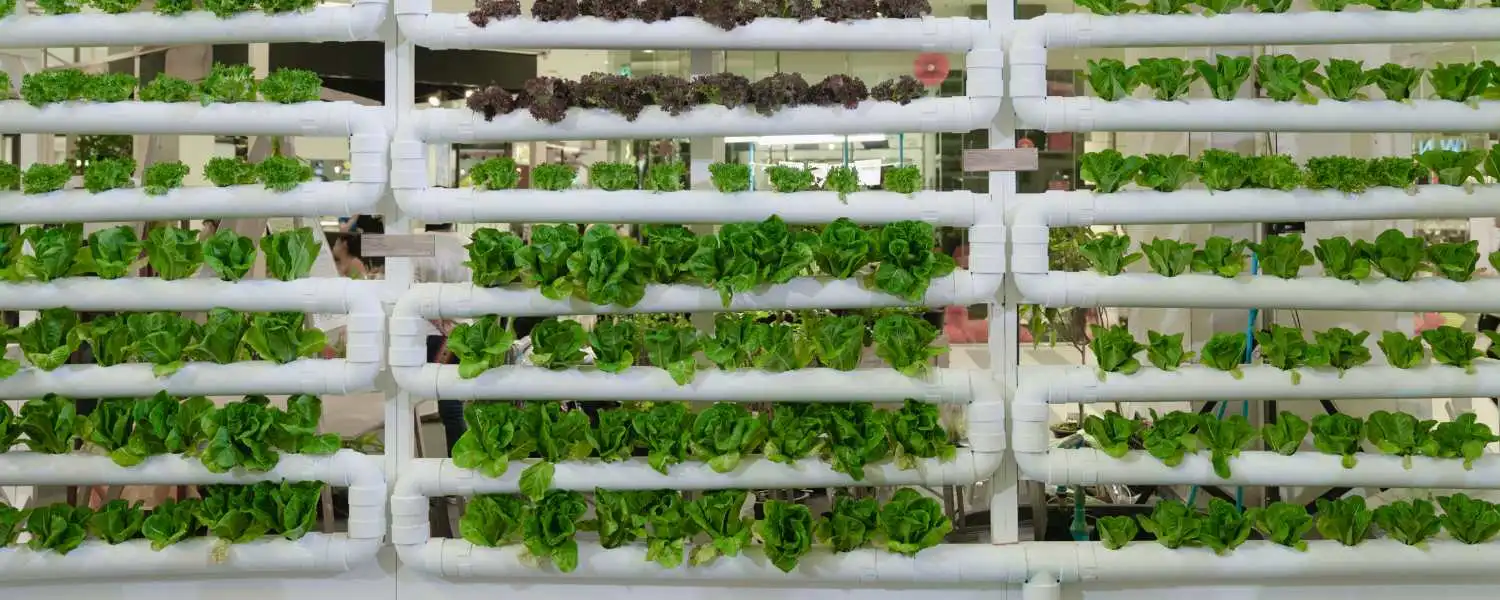

Vertical hydroponic systems, or DIY hydroponic systems, are innovative gardening setups that allow plants to grow vertically, maximising space and efficiency.
These systems are popular among urban gardeners and hobbyists with limited space for traditional gardening.
In a vertical hydroponic system, plants are grown in stacked layers or columns, with nutrient-rich water circulating to deliver essential nutrients directly to the plant roots.
This method eliminates the need for soil, as plants are suspended in an inert growing medium such as perlite or coconut coir.
DIY hydroponic systems are relatively easy to set up and maintain, making them accessible to beginners and experienced gardeners alike.
They can be constructed with PVC pipes, plastic containers, or recycled materials.
Vertical hydroponic systems offer several advantages, including increased crop yields, reduced water usage, and faster growth rates than traditional soil-based gardening.
Additionally, they can be customised to fit gardeners’ specific needs and preferences, allowing various plants to grow in a compact space.
Overall, DIY hydroponic systems are a practical and efficient way to grow plants indoors and outdoors, providing an accessible and sustainable gardening solution for urban environments.
9. PVC Pipe Hydroponic System
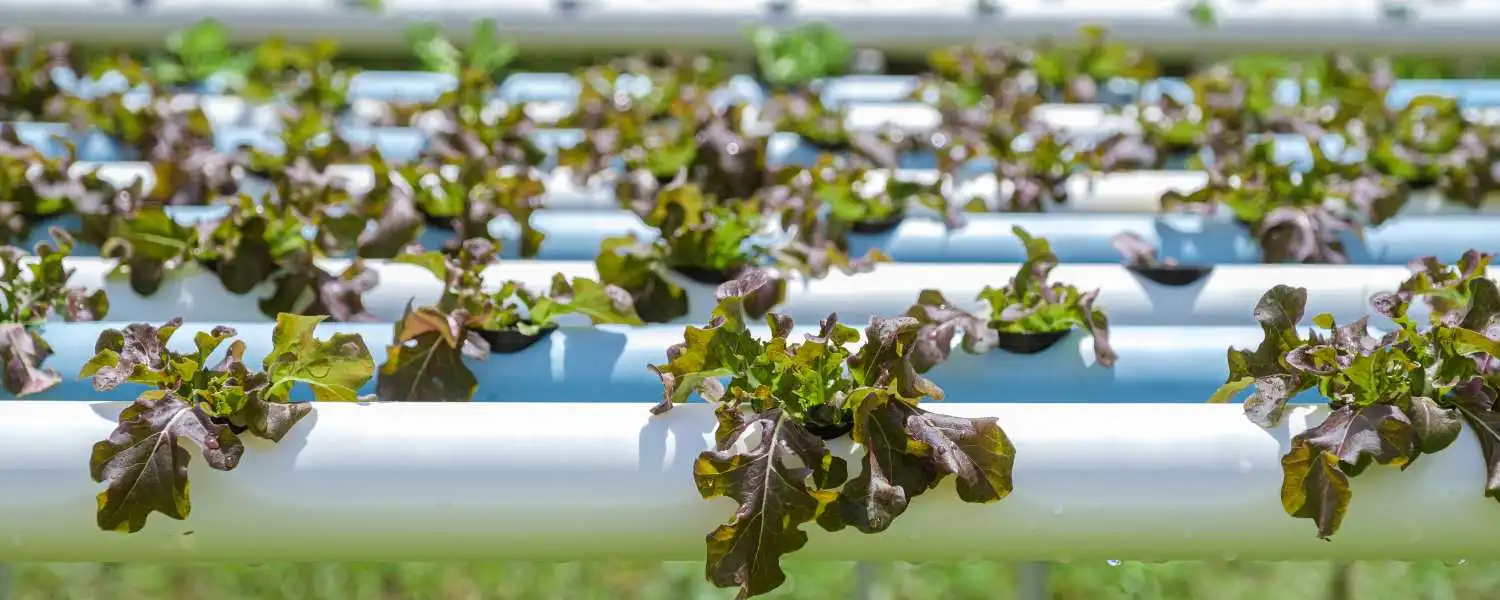

Due to its simplicity and affordability, a PVC pipe hydroponic system is a popular choice for DIY hydroponic systems.
This system utilises PVC pipes, which are available at hardware stores and are easy to work with.
To set up a PVC pipe hydroponic system, you will need PVC pipes, PVC connectors, a water pump, and a nutrient solution.
The PVC pipes are cut into equal lengths and arranged either horizontally or vertically, depending on space and layout.
Holes are drilled into the pipes to accommodate net pots or cups, which hold the plants in place.
The water pump then circulates the nutrient solution through the pipes, delivering essential nutrients directly to the plant roots.
This method allows for efficient nutrient uptake and oxygenation, promoting healthy plant growth.
PVC pipe hydroponic systems are versatile and can be customised to suit different plant types and growing environments.
Ideal for beginners or limited space, they need minimal maintenance and can be scaled up or down for different plant sizes.
Overall, PVC pipe hydroponic systems offer a simple and cost-effective solution for growing plants hydroponically at home.
10. Aquaponics
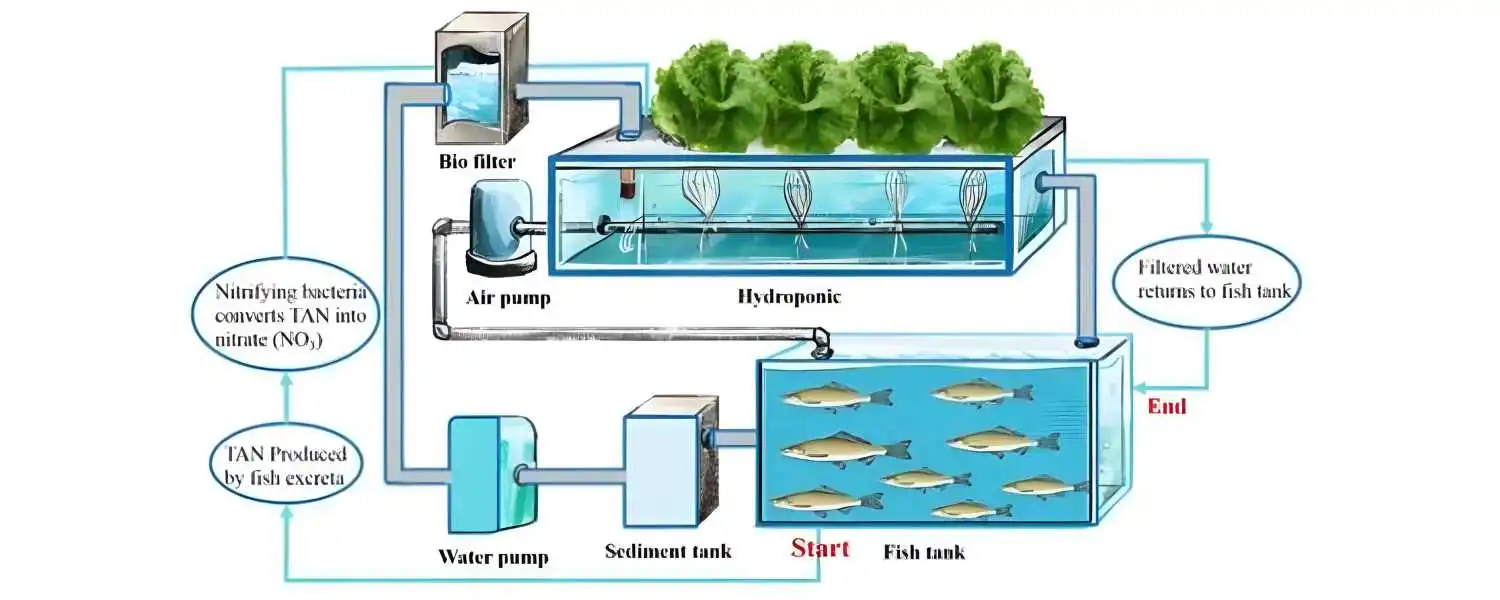
Aquaponics is an innovative gardening method that combines aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (growing plants in water).
In aquaponic systems, fish and plants grow together, with fish waste nourishing plants while plants purify water for fish.
This creates a closed-loop system where fish and plants benefit from each other’s presence.
DIY hydroponic systems are commonly used in aquaponics, cultivating plants in nutrient-rich solutions, bypassing soil.
The water from the fish tank is circulated through the hydroponic system, delivering essential nutrients to the plants.
As the plants absorb nutrients, they help purify the water to the fish tank. This creates a sustainable and efficient way to grow fish and plants in a small space.
Aquaponics gains popularity for producing fresh, healthy food in eco-friendly ways, appealing to gardeners and growers.
Aquaponic systems can be highly productive and rewarding for gardeners of skill levels with proper planning and maintenance.
11. Troubleshooting Common Issues

Setting up DIY hydroponic systems often leads to common growth issues affecting plants and system performance.
One common issue is nutrient deficiencies, where plants may need the proper balance of essential nutrients.
This can be addressed by regularly testing the nutrient solution and adjusting the nutrient levels.
Another common issue is pH imbalance, affecting nutrient availability and plant uptake.
Monitoring or adjusting the pH of the nutrient is essential to ensure optimal plant growth.
Also, improper lighting can be a problem, with plants either receiving too much or too little light.
Ensuring that plants receive a good amount of light for their growth stage is essential for healthy growth.
Finally, pest and disease infestations can occur in hydroponic systems, particularly if good hygiene practices are not followed.
Regularly inspecting plants for disease signs, removing affected ones, or applying organic pest control can prevent and manage issues.
Troubleshooting DIY hydroponic systems demands keen observation, maintenance, and proactive management for optimal plant growth.
12. Maintenance Tips for DIY Hydroponic Systems

Maintenance ensures successful plant growth for those venturing into DIY hydroponic systems.
Regularly monitoring the nutrient solution’s pH and nutrient levels is essential for plant health.
pH levels should ideally be maintained between 5.5 and 6.5 for optimal nutrient uptake.
Nutrient levels can be adjusted as needed to prevent deficiencies or toxicities.
Maintaining a clean reservoir prevents clogs and ensures proper nutrient circulation to plant roots.
Regularly check roots for rot or disease; prune dead or damaged roots to maintain plant health, and prevent pathogen spread.
Monitoring water temperature is crucial; warm water fosters oxygen deficiencies and harmful bacteria.
Finally, maintaining adequate lighting levels and ensuring proper ventilation helps promote healthy plant growth and prevents mould and fungal issues.
Following these maintenance tips, DIY hydroponic systems can thrive and produce healthy, vibrant plants for an enjoyable gardening experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DIY hydroponic systems provide a cost-effective method for soil-free plant cultivation, appealing to home gardeners.
Individuals can craft bespoke hydroponic systems using common materials and uncomplicated designs, aligning with their unique requirements.
Vertical farming systems offer increased crop yields, faster growth rates, and year-round plant cultivation, irrespective of outdoor climates.
Moreover, DIY hydroponic systems empower individuals to control food production and experiment with plant species and growing techniques.
DIY hydroponics offer flexibility, accessible to all gardeners.
Additionally, these systems promote sustainability by conserving water and reducing the need for chemical fertilisers, contributing to eco-friendly gardening practices.
DIY hydroponic systems offer valuable hands-on learning for all.
Individuals gain a deeper understanding of plant biology, nutrition, and environmental science by building and maintaining their hydroponic setups.
Components typically include containers, growing medium (e.g., perlite), nutrient solution, water reservoir, and a pump or wick for delivery.
For More Life-Hack Related Blogs subscribe to us now!
FAQ
Q1. What are DIY hydroponic systems?
A. DIY hydroponic systems are setups designed for cultivating plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water solutions instead.
These systems range from simple to complex, allowing enthusiasts to customise based on space, budget, and plant type.
Q2. Why choose DIY hydroponics?
A. DIY hydroponics offer numerous benefits, including space efficiency, water conservation, and accelerated plant growth.
By controlling nutrient levels and environmental factors, growers can optimise conditions for healthier plants and higher yields.
Q3. What materials are needed for a DIY hydroponic system?
A. Hydroponic systems feature containers, medium (perlite/clay), nutrients, reservoir, and delivery (pump/wick).
Depending on the system’s complexity, additional items like pH testers and grow lights may be required.
Q4. How difficult is it to set up a DIY hydroponic system?
A. While some setups may require technical skills, many DIY hydroponic systems can be assembled with essential tools and materials.
Numerous online resources, tutorials, and community forums offer guidance for beginners.
Q5. What can I grow in a DIY hydroponic system?
A. Any plant that thrives in soil can be grown hydroponically, including herbs, leafy greens, vegetables, and fruits.
Experimentation and adaptation are crucial to discovering what works best in your setup.