Introduction to High-Protein Vegetarian Diets
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in vegetarian diets driven by concerns for animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and health benefits. One common misconception about vegetarianism is the challenge of meeting protein needs without consuming meat.
However, with proper planning and food choices, individuals can quickly meet their protein requirements through a high-protein vegetarian diet.
Brief Overview of Vegetarianism and Protein Needs

Vegetarianism is the abstaining from consuming meat, poultry, and fish. Various forms of vegetarian diets exist, such as lacto-vegetarian, which incorporates dairy but excludes eggs; ovo-vegetarian, including eggs but excludes dairy; and lacto-ovo vegetarian, which encompasses both dairy and eggs.
There are also variations like pescatarian (which includes fish) and flexitarian (which is primarily vegetarian but occasionally consumes meat).
Protein is a crucial macronutrient required for various bodily functions, including building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining muscle mass.
The standard guideline for protein intake, known as the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA), suggests consuming 0.8 gram of protein per kilogram of body Weight loss diets per day for adults.
Regular exercise or strength training might necessitate increased protein consumption to facilitate muscle growth and repair.
Importance of Protein in a Vegetarian Diet

It’s crucial for vegetarians to maintain an ample protein intake in order to fulfill their nutritional requirements and bolster overall health.
Plant-based protein sources can provide all the essential amino acids required by the body, making them a valuable alternative to animal-derived proteins.
Furthermore, plant-based proteins generally contain lower levels of saturated fats and cholesterol, thus potentially contributing to improved cardiovascular health.
Benefits of High-Protein Vegetarian Diets
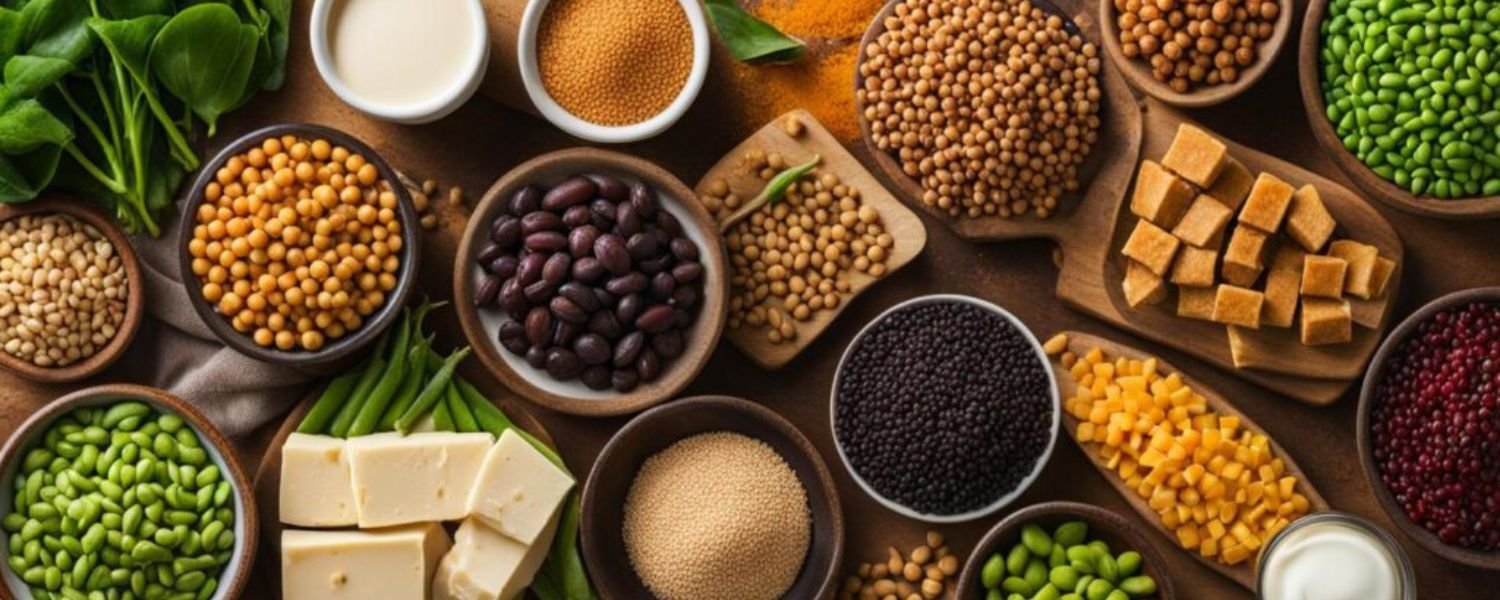

Incorporating a high-protein vegetarian diet into your lifestyle can offer a multitude of health benefits, supporting not only your fitness goals but also your overall well-being.
Here are some key advantages:
A. Muscle Building and Repair
Protein plays a pivotal role in fostering muscle growth and facilitating repair, rendering it indispensable for those actively involved in consistent exercise or strength training.
High-protein vegetarian diets provide ample amino acids for muscle synthesis, allowing you to build and maintain lean muscle mass effectively.
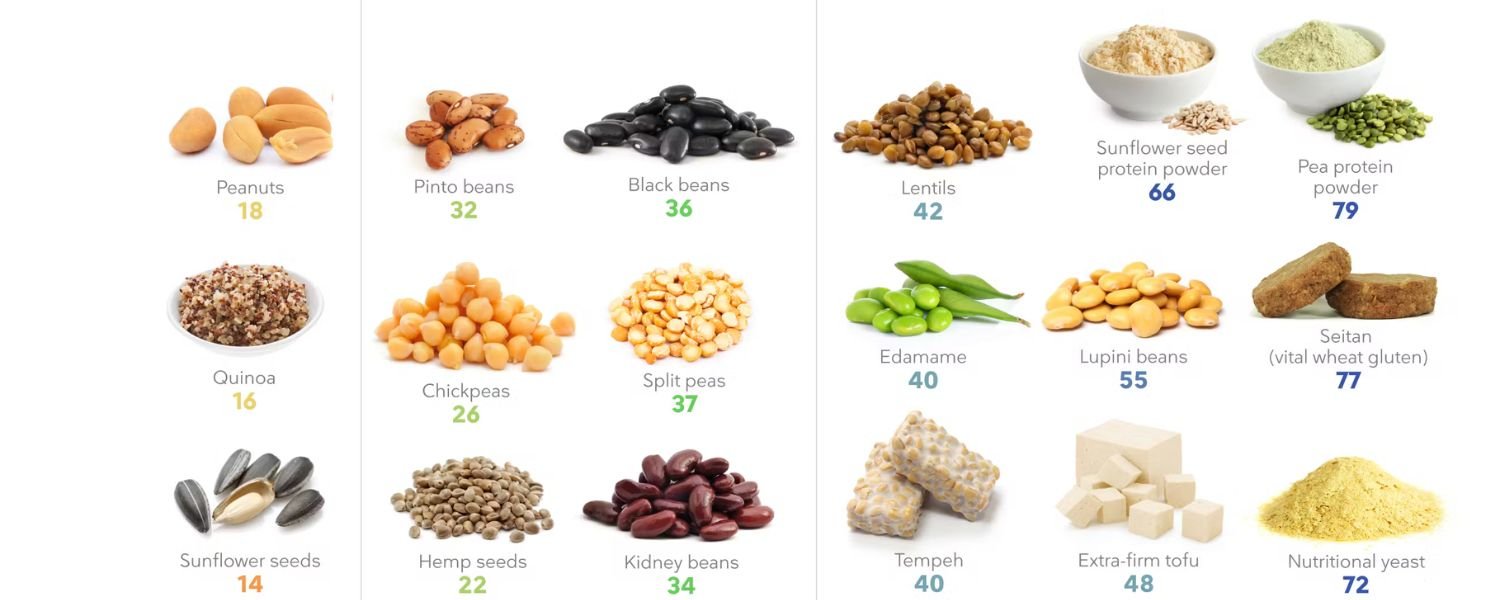
Legumes, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa are examples of plant-based protein sources that provide high-quality protein to enhance your fitness efforts.
B. Weight Management
Protein-rich vegetarian Fermented foods help promote feelings of fullness and satiety, aiding in weight management.
Incorporating protein into your meals helps curb cravings, reduces snacking, and supports healthy weight maintenance.
Plant-based proteins often have fewer calories and less saturated fat than animal proteins, making them a wise choice for calorie-conscious individuals.
C. Improved Satiety and Energy Levels
Consuming enough protein stabilizes blood sugar, prevents energy crashes, and improves focus and productivity. Protein-rich vegetarian meals curb hunger and provide lasting energy, keeping you energetic and attentive all day.
D. Support for Overall Health and Well-being
High-protein vegetarian diets support muscle growth, weight management, and overall health with fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
They reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. By prioritizing plant-based protein sources, you can enhance your nutritional intake and support long-term health.
Key Components of a High-Protein Vegetarian Diet
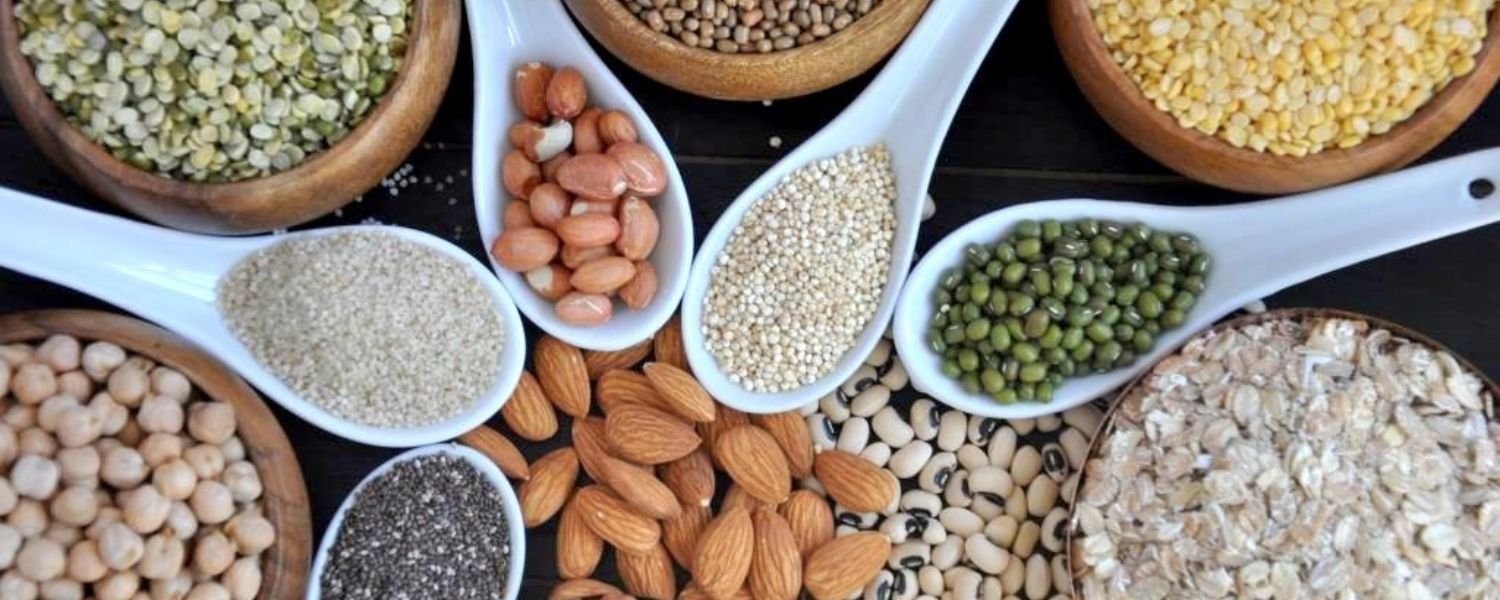

A high-protein vegetarian diet is feasible, but also nutritious and satisfying when properly planned. By incorporating various plant-based protein sources and nutrient-dense foods, you can meet your dietary needs while supporting your fitness goals.
Here are the critical components of a high-protein vegetarian diet:
A. Plant-Based Protein Sources
1. Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas offer an abundance of protein, fiber, and a wide range of nutrients, making them exceptional additions to a balanced diet. They can be used in multiple dishes, including soups, stews, salads, and curries.
2. Tofu and Tempeh: Tofu and tempeh, both derived from soy, offer versatile protein options that can be grilled, stir-fried, or baked, enhancing the texture and flavor of your dishes.
3. Edamame: Young soybeans, or edamame, are protein-packed and can be a delicious snack or added to salads and stir-fries.
4. Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, peanuts, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and flaxseeds are packed with protein, healthy fats, and essential nutrients.
These versatile foods can be incorporated into your diet in various ways, such as snacking on them, adding them to smoothies, or sprinkling them over oatmeal or yogurt for a nutritious boost.
5. Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, barley, oats, and bulgur are examples of whole grains that contain protein and provide a nutritious base for meals like grain bowls, salads, and pilafs.
6. Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Products like veggie burgers, veggie sausages, and plant-based meat substitutes made from soy, pea protein, or mushrooms offer convenient protein sources for vegetarians.
Incorporating a Variety of Foods for Balanced Nutrition

In addition to focusing on protein-rich foods, it’s essential to incorporate a variety of other food groups to ensure balanced nutrition.
Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nourishing fats into your meals to supply vital vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
1. Fruits and Vegetables: Strive to incorporate a diverse selection of colorful fruits and vegetables into your meals to enhance nutrient absorption and promote holistic well-being. Incorporate a mix of fresh, frozen, and canned options to ensure variety and convenience.
2. Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains in place of refined grains whenever feasible to capitalize on their elevated fiber content and supplementary nutrients. Experiment with different grains like quinoa, farro, and millet to diversify your meals.
3. Healthy Fats: Incorporate nutritious sources of healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds into your diet to supply essential fatty acids and promote heart health.
Utilize these fats when cooking, preparing salad dressings, or as flavorful toppings for various dishes.
4. Dairy or Dairy Alternatives: If you consume dairy, choose low-fat or non-fat options like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and skim milk.
For those who avoid dairy, there are numerous plant-based alternatives like almond milk, coconut yogurt, and soy cheese.
Meeting Macronutrient and Micronutrient Needs
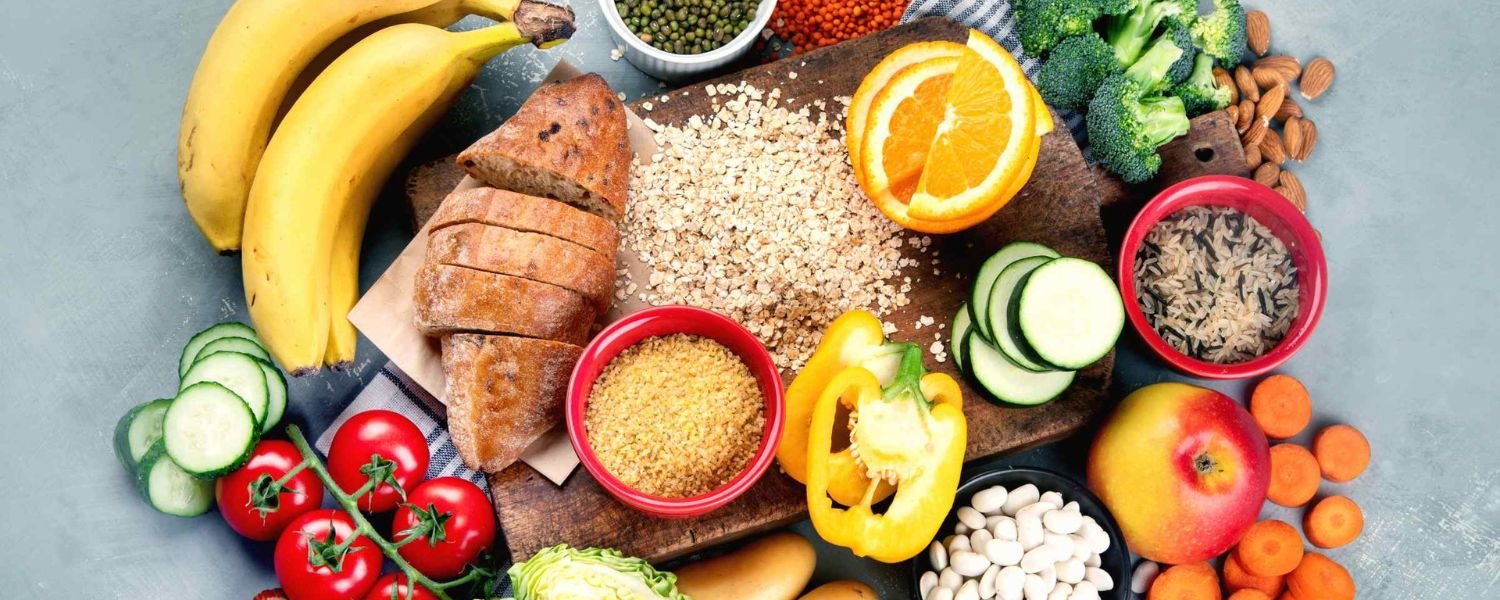

While protein is a crucial component of a high-protein vegetarian diet, it’s important to ensure you meet your overall macronutrient (carbohydrates and fats) and micronutrient (vitamins and minerals) needs.
Strive for a well-rounded diet comprising diverse foods from every food group, fostering optimal health and overall well-being.
1. Carbohydrates: Always choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes over simple carbohydrates like refined grains and sugars. These complex carbs provide sustained energy and essential nutrients.
2. Fats: Incorporate nourishing fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in moderate amounts to bolster brain function, regulate hormone production, and enhance nutrient absorption.
3. Vitamins and Minerals: Consume a diverse range of plant-based foods to ensure adequate vitamin and mineral intake. Consider supplementing with vitamin B12, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids if needed, especially for vegans.
4. Hydration: Ensure optimal hydration by consuming an ample amount of water consistently throughout the day. Herbal teas, infused water, and coconut water are refreshing alternatives that contribute to hydration.
Sample Meal Plan for a High-Protein Vegetarian Diet
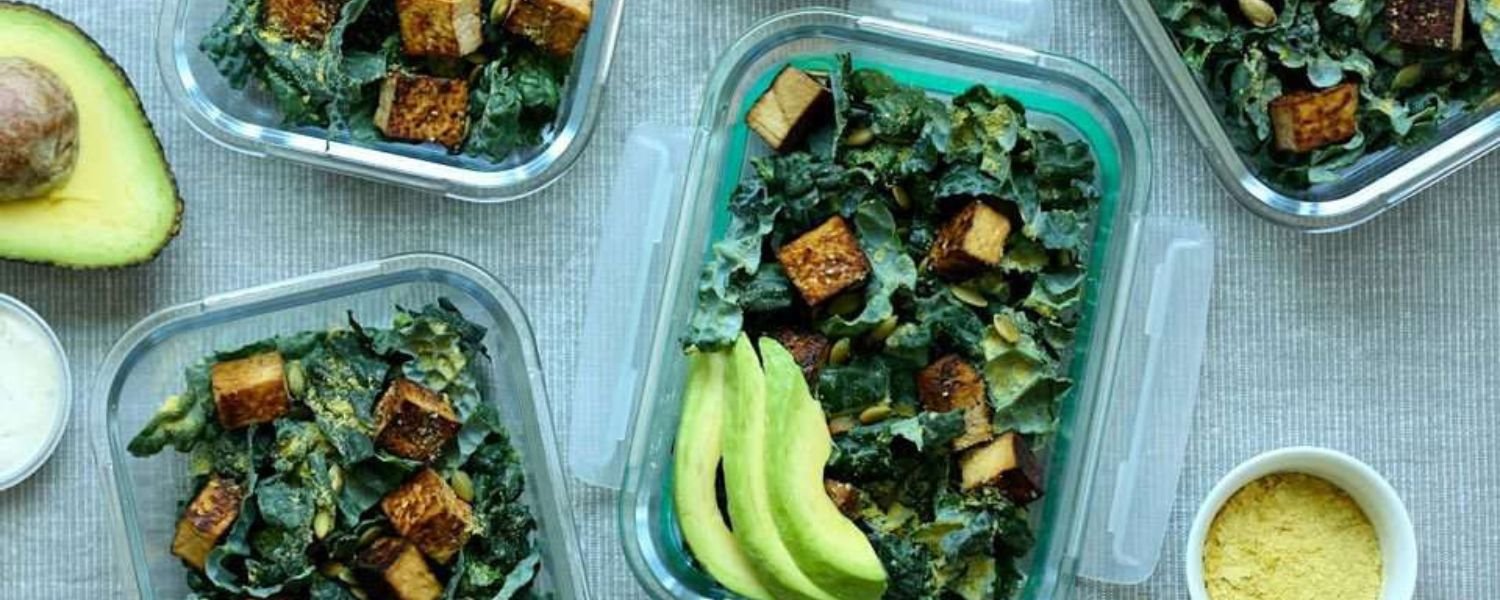

A. Breakfast options
1. Protein-packed smoothie: Combine spinach, banana, almond milk, protein powder, and a handful of berries in a blender for a nourishing and fulfilling breakfast option.
2. Greek yogurt parfait: Layer Greek yogurt with granola, mixed nuts, and fresh fruits like mango or papaya for a protein-rich morning meal.
B. Lunch ideas
1. Quinoa salad: Combine cooked quinoa with diced vegetables (such as bell peppers, cucumber, and cherry tomatoes), chickpeas, feta cheese, and a lemon-tahini dressing.
2. Lentil soup: Create a robust lentil soup infused with the vibrant flavors of carrots, celery, onions, and spinach, enhanced with a blend of aromatic herbs and spices.
C. Dinner recipes
1. Vegetable stir-fry with tofu: Sauté tofu with colorful vegetables in a savory sauce made with soy sauce, garlic, and ginger, served over brown rice.
2. Black bean tacos: Fill corn tortillas with seasoned black beans, avocado slices, shredded lettuce, diced tomatoes, and salsa for a delicious and protein-rich dinner option.
D. Snack suggestions
1. Roasted chickpeas: Mix cooked chickpeas with olive oil and seasonings such as cumin and paprika, then bake until they’re crispy for a delicious and satisfying snack.
2. Almond butter and apple slices: Spread almond butter on apple slices for a quick and nutritious snack that combines protein, healthy fats, and fiber.
Tips for Success

Adopting a high-protein vegetarian diet can be a rewarding journey that supports your fitness goals and overall health.
Here are some tips to help you succeed and make the most out of your dietary choices:
A. Meal Prep and Planning
1. Plan Ahead: Allocate some time to organize your meals for the week, covering breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks.
This proactive approach aids in maintaining structure and guarantees access to wholesome choices when hunger arises.
2. Batch Cooking: Prepare large batches of grains, beans, and protein sources like tofu or tempeh ahead of time. Store them in portioned containers in the fridge or freezer for quick and convenient weekly meals.
3. Prep Ingredients: Wash, chop, and portion out fruits, vegetables, and other ingredients in advance. Having prepped ingredients on hand will streamline meal preparation and make healthy eating more accessible.
B. Reading Food Labels and Identifying Protein-Rich Foods
1. Check Labels: When shopping for packaged foods, read the nutrition labels to identify protein content per serving. Look for products that provide a good amount of protein without excessive added sugars or unhealthy fats.
2. Focus on Whole Foods: Incorporate whole, minimally processed foods into your diet as much as possible.
Choose natural sources of protein such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains instead of depending heavily on processed vegetarian meat alternatives.
3. Experiment with New Ingredients: Explore different plant-based protein sources and try incorporating new foods into your meals regularly.
This will not only keep your meals exciting but also ensure that you’re getting a variety of nutrients in your diet.
C. Staying Hydrated
1. Drink Plenty of Water: Hydration is key to overall health and well-being. Incorporate the habit of drinking water consistently throughout the day, particularly prior to and following meals, during exercise sessions, and in warmer climates.
2. Infuse Flavor: If you find it challenging to consume plain water, consider infusing it with fresh fruits, herbs, or cucumber slices. This simple method adds natural flavor without introducing added sugars or calories.
3. Monitor Fluid Intake: Pay attention to signs of dehydration, such as thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, and dark-colored urine.
Aim to consume a minimum of 8-10 glasses of water each day, adjusting as needed if you engage in regular physical activity or reside in a warm environment
D. Seeking Guidance from a Nutritionist or Dietitian
1. Consult a Professional: If you’re just starting out with vegetarianism or feeling uncertain about meeting your nutritional requirements, it’s advisable to consult with a registered dietitian or nutritionist.
Their knowledge can guide you in crafting a personalized meal plan tailored to your needs. They’ll also address any concerns you may have and ensure that your diet provides all the essential nutrients necessary for your health and well-being.
2. Educate Yourself: Take the time to educate yourself about vegetarian nutrition and the importance of protein in your diet.
There are plenty of reputable resources, books, and websites available that provide valuable information and tips for success on a vegetarian diet.
3. Listen to Your Body: Listen closely to your body’s reactions to various foods and dietary decisions. If something feels off or if you’re noticing signs of nutrient deficiencies, don’t delay in seeking guidance from a professional. Making adjustments to your diet as needed can help ensure your overall well-being.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them

Transitioning to a high-protein vegetarian diet has challenges, but with the right strategies and mindset, you can thrive.
Here are some common challenges and practical tips to help you navigate them effectively:
A. Addressing Concerns About Protein Intake
1. Educate Yourself: Recognize that plant-based protein sources offer a complete array of essential amino acids necessary for your body’s optimal functioning. Learn about vegetarian protein sources and diversify your meals for sufficient intake.
2. Prioritize Protein: Make an effort to include protein-rich foods in every meal and snack. Concentrate on incorporating legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, lentils, beans, seeds, and whole grains into your diet to increase your protein consumption and fulfill your nutritional requirements.
3. Supplement if Necessary: Consider incorporating plant-based protein powders or protein supplements into your diet, especially if you have increased protein requirements due to intense physical activity or specific health goals.
B. Dealing with Cravings and Temptations
1. Plan Ahead: Anticipate cravings and temptations by planning satisfying and nutritious meals and snacks in advance.
Ensuring that nutritious choices are easily accessible can aid in resisting unhealthy temptations and opting for more wholesome foods.
2. Find Alternatives: Experiment with vegetarian versions of your favorite dishes or snacks to satisfy cravings without compromising your dietary goals.
For example, try making veggie burgers, homemade pizza with tofu or tempeh toppings, or roasted chickpeas as a crunchy snack.
3. Practice Mindful Eating: Be mindful of your body’s signals for hunger and satisfaction, practicing attentive eating to prevent impulsive snacking or excessive consumption.
Slow down and relish each mouthful, immersing yourself in the tastes and sensations of your food.
C. Handling Social Situations and Dining Out
1. Communicate Your Dietary Preferences: Inform friends, family members, and restaurant staff about your dietary preferences and restrictions in advance.
Consider volunteering to bring a dish to social gatherings, or recommend vegetarian-friendly restaurants where everyone can enjoy a satisfying meal.
2. Be Flexible: While sticking to your dietary principles is important, it’s also essential to be flexible and adaptable in social situations. Focus on making the best choices available to you without feeling restricted or deprived.
3. Explore Global Cuisine: Embrace the diversity of vegetarian cuisine from around the world and explore traditional dishes from cultures that have a rich history of plant-based eating. You’ll discover a wealth of flavorful and satisfying options to enjoy.
Follow these methods to overcome the challenges of a high-protein vegetarian diet, ensuring a confident and satisfying nutritional journey.
Remember to stay patient and persistent, and celebrate your progress. With time and practice, you’ll develop habits that support your health and well-being for the long term.
Conclusion
Adopting a high-protein vegetarian diet provides health benefits such as muscle support, weight management, and increased satiety.
Incorporating diverse plant-based proteins and nutrient-rich foods helps meet protein needs effectively. With the right planning and strategies, transitioning to this healthy, fulfilling lifestyle is achievable.
For More Health-Related blogs, subscribe to us now!
FAQ
Q1. What are some high-protein vegetarian foods?
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, black beans)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, hemp seeds)
- Quinoa and other whole grains
- Greek yogurt and cottage cheese
Q2. Can a high-protein vegetarian diet help with weight loss?
A. Yes, sufficient protein in a vegetarian diet can help manage weight by increasing fullness and reducing calorie intake.
A high-protein vegetarian diet can support weight loss goals combined with regular exercise.
Q3. Are there any traditional Indian fruits that are high in protein?
A. Traditional Indian fruits like guava, jackfruit, and avocado provide protein, vitamins, and minerals, despite generally low protein content in fruits.
Q4. What are some popular fermented foods in traditional Indian cuisine?
A. Traditional Indian cuisine includes various fermented foods such as dosa, idli, dhokla, and pickles (achar), which are not only flavorful but also provide probiotics that support gut health.
Q5. Are there specific belly fat exercises recommended for individuals on a high-protein vegetarian diet?
A. Spot reduction is a myth, but exercises like planks, Russian twists, and bicycle crunches can strengthen abs and help reduce belly fat alongside a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Q6. What types of exercises are effective for weight loss?
A. Effective exercises for weight loss encompass a range of activities, including cardiovascular exercises like walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming.
Strength training regimens are also highly effective, promoting the development of lean muscle mass, which in turn boosts metabolism.