Introduction
When you think of insects, the image of a stag beetle might not be the first to come to mind. However, this fascinating beetle is truly a warrior of the insect world.
With its impressive size, unique features, and intriguing behavior, the stag beetle is a creature that captures the imagination of many. In this article, we’ll explore the world of the stag beetle, including its evolution, antler allometry, and much more.
Whether you’re curious about its diet, habitat, or uses, we’ve got you covered.
Overview

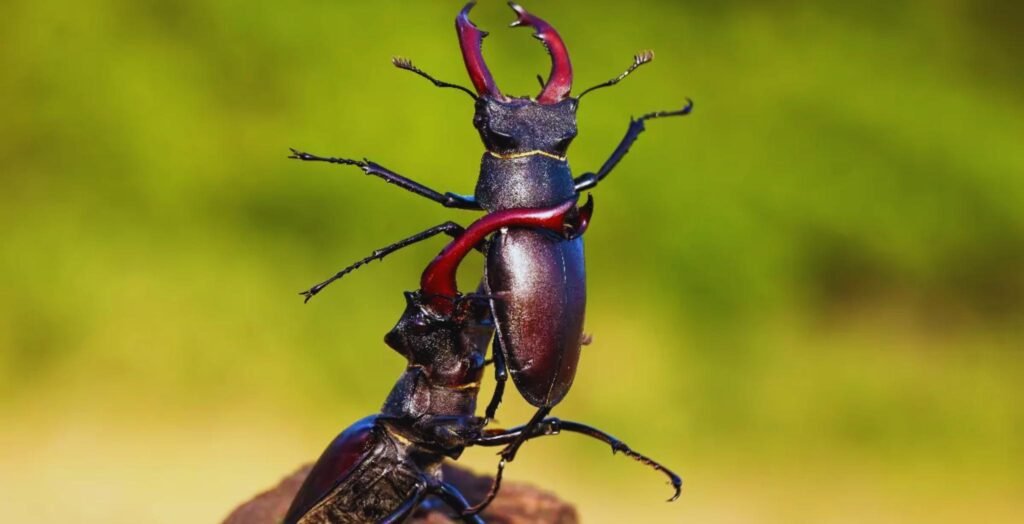
The stag beetle is a member of the family Lucanidae, known for its distinctive appearance and impressive size. The name “stag beetle” comes from the large, antler-like mandibles (jaws) that resemble the antlers of a stag.
These mandibles are primarily used in combat with other stag beetles, especially during mating battles.
Stag beetles are found in various parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, and North America. In India, stag beetles are less common but can still be spotted in certain regions.
The beetle’s body is typically dark brown or black, and its mandibles can be quite large, especially in males. The female stag beetle is generally smaller and lacks the large mandibles seen in males.
One interesting aspect of stag beetles is their impressive lifespan. They can live for several years in their larval stage, and their adult life can last for up to a year.
During their lifetime, stag beetles go through a complete metamorphosis, including the egg, larval, pupal, and adult stages.
Evolution

The evolution of the stag beetle is a fascinating topic. These insects have been around for millions of years, with their ancestors dating back to the Jurassic period. Over time, they have evolved a variety of traits that have helped them survive and thrive in different environments.
The large mandibles of the stag beetle are a key evolutionary feature. These mandibles are believed to have evolved primarily for combat with other males.
During mating season, males use their mandibles to fight for dominance and the right to mate with females. This behavior is thought to have driven the evolution of larger and more robust mandibles.
In addition to their mandibles, stag beetles have evolved a range of other adaptations. For example, their body structure allows them to climb and navigate through their forest habitats with ease.
They are also equipped with strong legs and a tough exoskeleton, which help them survive in their environment.
Antler allometry

Antler allometry refers to the study of the relationship between the size of an animal’s antlers (or in this case, mandibles) and its overall body size. In stag beetles, the size of the mandibles is an important factor in determining their fitness and success in mating.
Male stag beetles have particularly large mandibles compared to females. This is because the mandibles are used in combat with other males. The larger the mandibles, the more likely a male is to win fights and secure a mate.
This phenomenon is known as sexual dimorphism, where males and females of a species have different physical traits.
The size of the mandibles is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. In some cases, the availability of food and other resources can impact the growth of the mandibles.
For example, a beetle that has access to a rich food supply during its larval stage may develop larger mandibles as an adult.
Researchers have studied the relationship between mandible size and overall body size in stag beetles to better understand how these traits are linked.
Conclusion
The stag beetle is truly a mighty warrior of the insect world. Its impressive mandibles, unique evolutionary traits, and fascinating behavior make it a remarkable creature.
From its origins millions of years ago to its role in today’s ecosystems, the stag beetle is a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of insects.
If you’re interested in learning more about stag beetles, there are many resources available that cover topics such as stag beetle diet, stag beetle larvae, and stag beetle habitat.
For example, they are sometimes kept as pets in certain cultures, and their impressive appearance can make them a fascinating addition to an insect collection.
So, whether you’re a budding entomologist or just curious about the world of insects, the stag beetle is a creature worth exploring. With its powerful mandibles and rich evolutionary history, it stands as a true warrior in the insect world.
For more educacational related blogs subscribe us.
FAQ
Q. What is a stag beetle?
A. stag beetle is an insect known for its large, antler-like mandibles that resemble a stag’s antlers. These mandibles are primarily used for fighting with other males during mating season.
They are members of the family Lucanidae and are found in various regions, including Europe, Asia, and North America.
Q. Where can you find stag beetles?
A. Stag beetles are found in various parts of the world. In the Europe and North America, they are common in forested and wooded areas.
In the Asia, they inhabit a range of environments, including tropical forests. In India, stag beetles are less common but can be spotted in certain regions with suitable habitats.
Q. What do stag beetles eat?
A. The diet of stag beetles varies depending on their life stage. Adult stag beetles primarily feed on tree sap and decaying wood. Stag beetle larvae feed on rotting wood and organic matter in the soil. They help break down dead wood and contribute to nutrient recycling in their habitats.
Q. How do stag beetles reproduce?
A. During the mating season, male stag beetles use their large mandibles to fight other males for the right to mate with females. The winner of these battles is more likely to secure a mate.
After mating, the female lays eggs in decaying wood or soil, where the larvae will develop.
Q. What are stag beetle larvae like?
A. Stag beetle larvae are white, worm-like creatures that live in decaying wood or soil. They feed on organic matter and grow for several years before pupating and emerging as adults.
The larval stage is crucial for their development, and they can live in this stage for up to 3-4 years.