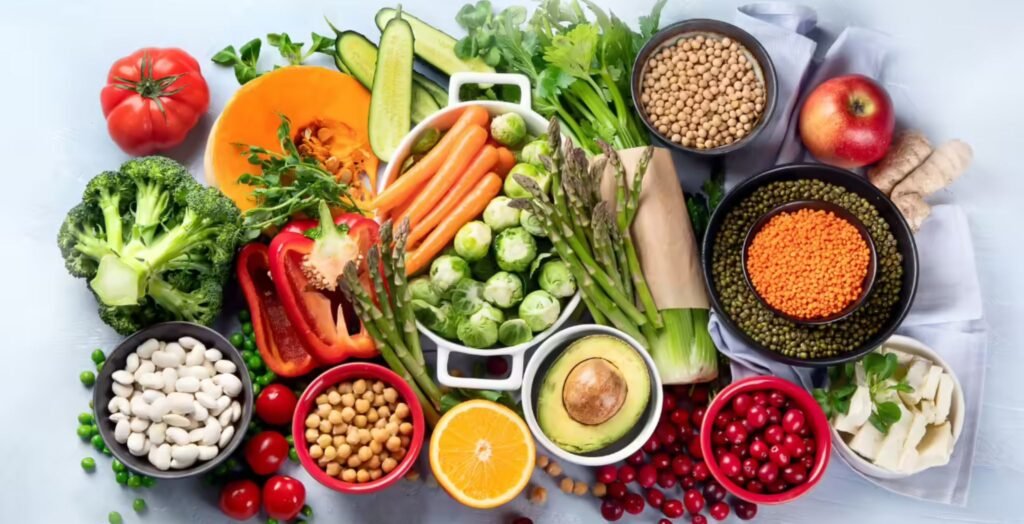
Embark on a journey of health and sustainability with our comprehensive guide to crafting the perfect vegan diet plan.
Vegan Diet

Veganism isn’t just a diet; it’s a lifestyle choice that refrains from any involvement in the exploitation or harm of animals, including food, clothing, and other products.
A vegan diet is entirely plant-based, avoiding meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, and honey. Instead, it emphasizes fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
1. Health Benefits of Veganism
Switching to a vegan diet can have significant health benefits. Studies indicate that individuals following a vegan diet often exhibit lower cholesterol levels, a diminished susceptibility to heart disease, reduced blood pressure, and a lower probability of developing type 2 diabetes.
Furthermore, a well-planned vegan diet can provide all the necessary nutrients, including protein, vitamins, and minerals, while promoting Weight loss and overall well-being.
2. Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Veganism extends beyond personal health to environmental and ethical considerations. Animal agriculture plays a substantial role in environmental deterioration, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution.
Opting for a vegan lifestyle allows individuals to lessen their environmental impact and foster a more sustainable future.
Additionally, veganism aligns with ethical principles of compassion and non-violence towards animals, advocating for their welfare and liberation from exploitation.
Understanding the Basics of a Vegan Diet

A. Food Groups in a Vegan Diet
A vegan diet encompasses various plant-based foods that provide essential nutrients for optimal health. These food groups include:
1. Fruits and Vegetables: Abundant in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables serve as the cornerstone of a vegan diet. They offer diverse flavors, textures, and colors, making nutritious and visually appealing meals.
2. Legumes: Legumes such as beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas are versatile plant-based protein sources. They are also high in fiber, folate, potassium, and iron, making them valuable components of a balanced vegan diet.
3. Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds offer healthy fats, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds are nutrient powerhouses that can seamlessly enhance your meals, snacks, or serve as delicious toppings.
B. Essential Nutrients to Focus on
While a carefully structured vegan diet can furnish all necessary nutrients, there are specific key nutrients that require special attention among vegans:
1. Protein: Plant-based protein sources include legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, soy products, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Consuming various protein-rich foods throughout the day ensures an adequate intake of essential amino acids.
2. Calcium: Incorporating calcium-rich plant foods into your meals and snacks can help meet your calcium needs. These foods include plant milks and orange juice fortified with calcium, tofu made using calcium sulfate. Additionally, almonds and sesame seeds are good sources of calcium.
3. Iron: Plant-based iron sources include lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, spinach, fortified cereals, quinoa, and pumpkin seeds. Including vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli in your meals alongside iron-rich foods can boost iron absorption.
4. Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is predominantly present in animal-derived foods, making it essential for vegans to acquire it from fortified sources like plant-based milks, breakfast cereals, and nutritional yeast, or through supplementation to prevent deficiencies.
5. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and supplements derived from algae are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, crucial for maintaining the health of both the heart and the brain.
C. Common Sources of Plant-Based Protein, Calcium, Iron, etc.
1. Plant-based Proteins include legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), tofu, tempeh, edamame, seitan, soy milk, nuts, seeds, quinoa, and whole grains.
2. Calcium: Fortified plant milks (soy, almond, oat), fortified orange juice, tofu set with calcium sulfate, leafy greens (kale, collard greens), almonds, sesame seeds, and figs.
3. Iron: Lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, spinach, fortified cereals, quinoa, pumpkin seeds, and dried apricots.
4. Vitamin B12: Fortified plant milks, breakfast cereals, nutritional yeast, and B12 supplements.
5. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and algae-based supplements.
Creating Your Vegan Diet Plan

A. Setting Your Goals and Objectives
Before embarking on a vegan diet plan, it’s essential to establish clear goals and objectives. Consider the following steps:
1. Identify Your Motivation: Whether it’s improving health, promoting environmental sustainability, or aligning with ethical values, understanding your reasons for adopting a vegan lifestyle will help you stay committed.
2. Set Realistic Goals: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that reflect your aspirations. For example, you might aim to incorporate more plant-based meals into your diet, transition to a fully vegan diet over time, or achieve a certain level of exercise for Weight Loss.
3. Consider Your Dietary Preferences and Restrictions: When setting your goals, consider any dietary preferences, allergies, or intolerances. Veganism offers flexibility and can accommodate various culinary traditions and taste preferences.
4. Seek Support and Accountability: Share your goals with supportive friends, family members, or online communities who can offer encouragement, advice, and accountability throughout your journey.
B. Designing Balanced Meals and Snacks
Designing balanced vegan meals and snacks is key to meeting your nutritional needs and sustaining energy levels throughout the day. Here are some tips:
1. Prioritize Whole Foods: Build your meals using primarily whole, minimally processed plant-based ingredients like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These nutrient-dense foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
2. Include a Variety of Colors and Textures: Strive to include a wide variety of fruits and vegetables in your meals. Each of them brings its distinct palette of colors, flavors, and textures. This diversity ensures that you receive a wide range of essential nutrients and beneficial phytochemicals.
3. Incorporate Protein-Rich Foods: Include plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, edamame, chickpeas, seitan, and vegan protein powders in your meals to support muscle repair and maintenance.
4. Don’t Forget Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, into your meals to promote satiety and support brain and heart health.
5. Balance Macronutrients: Ensure that each meal contains a balanced combination of carbohydrates, protein, and nutritious fats. This balanced approach not only sustains energy levels but also promotes overall health and well-being.
6. Plan Snacks Mindfully: To keep hunger at bay between meals, choose nutrient-rich snacks like fresh fruit, raw vegetables with hummus, whole grain crackers with nut butter, or homemade energy balls.
C. Meal Prepping and Planning Tips
Meal prepping and planning can streamline your vegan diet plan and make healthy eating more convenient and accessible. Consider the following strategies:
1. Schedule Weekly Meal Planning Sessions: Allocate a specific time each week to plan your meals, make a shopping list, and prepare ingredients. This practice will keep you organized and alleviate decision-making stress, especially on hectic weekdays.
2. Batch Cook Staples: Prepare large batches of grains, legumes, roasted vegetables, and sauces in advance and portion them into containers for easy assembly into meals throughout the week.
3. Invest in Quality Storage Containers: Invest in various reusable containers in different sizes to safely store prepped ingredients, leftovers, and meals in the fridge or freezer.
4. Prep Grab-and-Go Options: Prepare grab-and-go snacks and meals such as overnight oats, chia pudding, pre-portioned smoothie packs, chopped fruit, and pre-made salads for busy days when time is limited.
5. Utilize Freezing: Freeze leftover meals, soups, stews, and sauces in individual or family-sized portions for quick and convenient meals on hectic days.
6. Stay Flexible and Adapt: Flex your meal plan and adapt it based on changing schedules, ingredient availability, and culinary inspiration. Experiment with new recipes, flavors, and ingredients to keep meals exciting and enjoyable.
By setting clear goals, designing balanced meals and snacks, and implementing efficient meal-prepping and planning techniques, you can create a sustainable and enjoyable vegan diet plan that aligns with your health, lifestyle, and values.
Sample Vegan Diet Plans

A. Meal Plans for Different Caloric Needs
Vegan Diet Plan for Weight Loss Fast (1500 calories per day)
Day 1
Breakfast: Whole grain bread, toasted to perfection and topped with a luscious spread of mashed avocado and fresh, juicy tomato slices.
Lunch: Quinoa salad with mixed greens, roasted vegetables, chickpeas, and lemon-tahini dressing.
Dinner: Baked tofu with steamed broccoli and quinoa.
Snack: Carrot sticks with hummus.
Day 2
Breakfast: Toasted whole grain bread topped with creamy mashed avocado and fresh slices of tomato.
Lunch: Lentil soup with spinach and whole grain crackers.
Dinner: Zucchini ribbons topped with marinara sauce and plant-based meatballs.
Snack: Apple slices with almond butter.
Day 3
Breakfast: Smoothie made with spinach, banana, frozen berries, almond milk, and protein powder.
Lunch: A delicious dish featuring a base of nutty brown rice, topped with hearty black beans, roasted sweet potatoes, creamy avocado, and zesty salsa.
Dinner: Stir-fried tempeh with mixed vegetables and brown rice.
Snack: Crunchy rice cakes generously spread with creamy peanut butter and topped with slices of fresh strawberries.
B. Day-to-Day Meal Plans for Breakfast, Lunch, Dinner, and Snacks
Day 1
Breakfast: Vegan tofu scramble with sautéed spinach, tomatoes, and whole grain toast.
Lunch: Chickpea salad wrap with mixed greens, cucumber, tomato, and hummus.
Dinner: Vegan lentil curry with brown rice and steamed broccoli.
Snack: Mixed nuts and dried fruit.
Day 2
Breakfast: Smoothie bowl topped with granola, sliced banana, and shredded coconut.
Lunch: Quinoa and black bean salad with avocado, corn, bell peppers, and lime-cilantro dressing.
Dinner: Spaghetti squash with marinara sauce, vegan meatballs, and a side salad.
Snack: Sliced apple with almond butter.
Day 3
Breakfast: Vegan protein pancakes with maple syrup and mixed berries.
Lunch: Buddha bowl with roasted sweet potatoes, Brussels sprouts, chickpeas, and tahini dressing.
Dinner: Vegan chili with kidney beans, diced tomatoes, onions, and bell peppers.
Snack: Carrot sticks with hummus.
C. Seasonal Meal Plans for Variety and Freshness
1. Spring
Breakfast: Berry smoothie with spinach, banana, almond milk, and hemp seeds.
Lunch: Asparagus and pea risotto with lemon zest and vegan parmesan.
Dinner: Grilled portobello mushrooms with quinoa pilaf and roasted spring vegetables.
Snack: Fresh strawberries and snap peas.
2. Fall
Breakfast: Pumpkin spice overnight oats with pecans and maple syrup.
Lunch: Butternut squash soup with crusty whole grain bread and a side salad.
Dinner: Vegan stuffed acorn squash with wild rice, cranberries, and walnuts.
Snack: Baked apple slices with cinnamon.
Tips for Success and Sustainability

Transitioning to and maintaining a vegan lifestyle can be rewarding and fulfilling with the right strategies. Here are some tips to help you succeed and sustain your vegan journey:
A. Overcoming Common Challenges
1. Start Gradually: If transitioning to a vegan diet feels overwhelming, gradually incorporate more plant-based meals into your routine. Focus on adding rather than restricting foods initially.
2. Educate Yourself: Learn about vegan nutrition, cooking techniques, and ingredient substitutions to feel confident and empowered in your food choices.
3. Find Vegan Alternatives: To ease the transition, discover vegan versions of your favorite foods and ingredients, such as plant-based meats, dairy-free cheeses, and egg substitutes.
4. Stay Prepared: Plan by stocking your pantry with staple vegan ingredients, preparing snacks and meals in advance, and carrying portable snacks when on the go to avoid feeling tempted by non-vegan options.
B. Staying Motivated and Inspired
1. Connect with Like-Minded Individuals: Seek support from friends, family, online communities, or local vegan groups to share experiences, recipes, and tips and stay motivated on your vegan journey.
2. Explore New Foods and Recipes: Experiment with various fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, and try out different cooking methods and cuisines to keep meals exciting and diverse.
3. Celebrate Successes: Celebrate milestones and achievements along the way, whether it’s trying a new vegan recipe, reaching a health or fitness goal, or making a positive impact on the environment.
4. Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on vegan news, developments, and resources to stay inspired and informed about the latest vegan products, initiatives, and advocacy efforts.
C. Finding Supportive Communities and Resources
1. Utilize Online Resources: Explore vegan websites, blogs, social media accounts, and forums for recipe inspiration, meal ideas, nutritional guidance, and support from the global vegan community.
2. Attend Vegan Events and Workshops: Attend vegan festivals, cooking classes, and workshops to connect with like-minded individuals, learn new skills, and discover innovative plant-based products and practices.
3. Support Vegan-Friendly Businesses: Support businesses that embrace vegan-friendly options, including restaurants, cafes, grocery stores, and food brands, to demonstrate solidarity with your values and bolster the expansion of the vegan movement.
Conclusion
Embracing a vegan lifestyle offers numerous health, environmental, and ethical benefits. With proper planning and creativity, anyone can enjoy a varied and nutritious plant-based diet.
Whether aiming for weight loss, improved health, or simply exploring new culinary horizons, a vegan diet plan can be fulfilling and sustainable.
For more health-related blogs, subscribe us!
FAQ
Q. Are vegan diets suitable for weight loss?
Yes, vegan diets can effectively lose weight when they emphasize whole, plant-based foods and portion control.
Including a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains in your meals, limiting consumption of processed foods and added sugars while focusing on whole, minimally processed foods, can aid in achieving your weight loss objectives.
Q. How can I get enough protein on a vegan diet?
Plenty of plant-based protein sources include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds. Incorporating various foods throughout the day can help you meet your protein needs.
Q. Can I follow a vegan diet if I have cultural or traditional dietary preferences?
Absolutely! Veganism can be adapted to various cultural and traditional cuisines. Explore plant-based versions of your favorite dishes and incorporate ingredients commonly used in your culture’s cuisine.